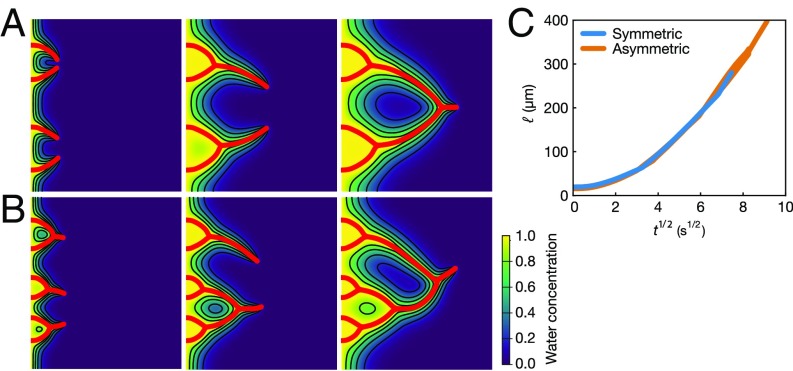
Fig. 4.
Results from the numerical simulations in which the red lines show the trajectories of the branches and the contours map the water concentration field. Oil droplets form on the branches, and thus the water concentration in the region near the branches is highest. (A) Symmetric case with four identical initial perturbations at . (B) Asymmetric case with six different initial perturbations at . (C) Regardless of whether the branches are symmetric or not, their tips follow very similar diffusion-dominated behavior, as seen from the linear scaling governing the distance between the tips and the left boundary beyond the initial transient, similar to that observed in Fig. 3C.