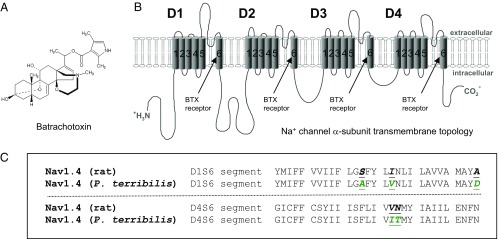
Fig. 1.
(A) Chemical structure of batrachotoxin. (B) Transmembrane topology of the voltage-gated Na+ channel α-subunit. The cylinders embedded in the lipid bilayer represent the transmembrane α-helical segments (S1–S6) of domains D1–D4. Arrows indicate the BTX receptor at the inner cavity. (C) AA sequences within D1/S6 and D4/S6 of the muscle Na+ channel (Nav1.4) from R. norvegicus and P. terribilis. Five AA substitutions in D1/S6 and D4/S6 of P. terribilis muscle Na+ channel (9) are highlighted in green.