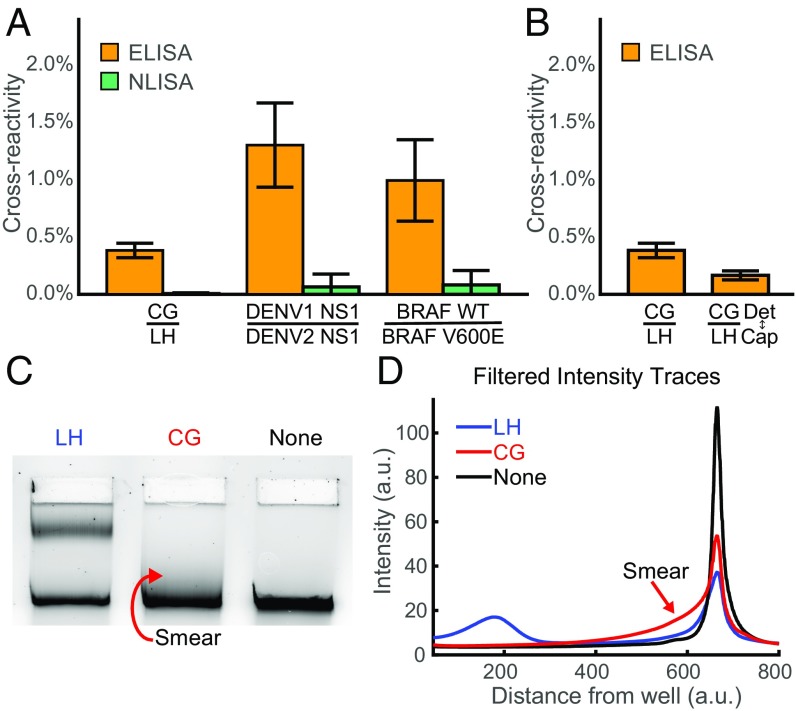
Fig. 4.
Low cross-reactivity for NLISA. (A) Cross-reactivity of NLISA compared with ELISA given by the ratio of the signal from 1 nM nontarget protein to 1 nM target protein. Results are shown for cross-reactivity to chorionic gonadotropin (CG) in an assay for luteinizing hormone (LH) (P = 1.6 × 10−4), to dengue virus serotype 1 nonstructural protein 1 (NS1) in an assay for dengue virus serotype 2 NS1 (P = 1.6 × 10−4), and to wild-type B-Raf in an assay for mutant B-Raf V600E (P = 0.017). Error bars are the SEM for eight replicates, and the P values are given by a Wilcoxon rank-sum test. (B) Cross-reactivity of ELISA for CG to LH for both cases of each antibody used in either capture or detection. Error bars are the SEM for eight replicates. (C) Representative gel image of NLISA using antibodies against LH to assay 1 nM of LH, 1 nM of CG, and a control lane lacking any target in 20% FBS. Looping is observed when the antibody pair on the nanoswitch strongly bind the target protein LH, while a smear is observed when the antibody pair only weakly binds the off-target protein CG target. (D) Representative filtered intensity traces in the presence of LH or CG, and also a control lane with neither.