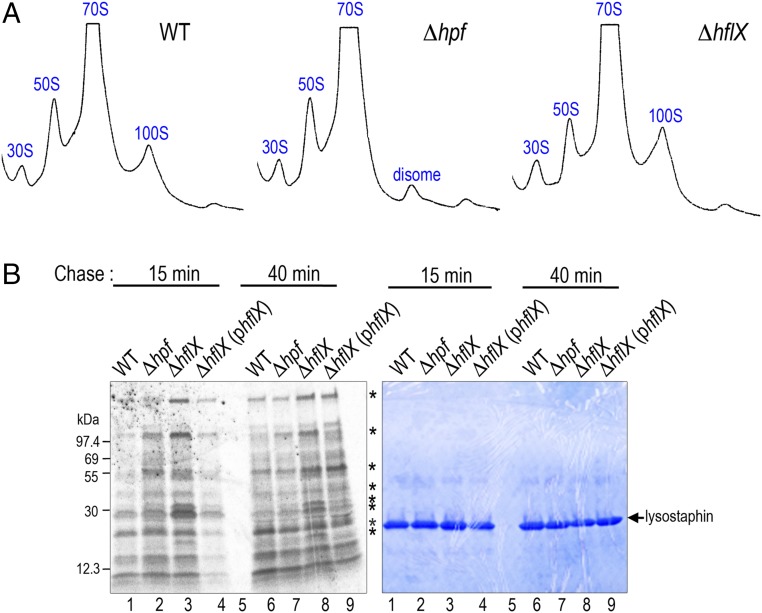
Fig. 5.
In vivo contribution of HflX during 47 °C growth. (A) Ribosome profiles of S. aureus JE2 and its hpf, hflX null mutants. A ΔhflX null deficient in ribosome dissociation has more 70S and 100S particles than the wild-type (WT). Ribosome species were analyzed on a 5–25% sucrose density gradient (x axis) and the absorbance was monitored at 254 nm (y axis). Each panel represents 2.5 Abs260 units of RNA input. (B) Pulse-chase analysis showing a reduction of translational capacity in the WT and the ΔhflX (phflX) complementing strain at 47 °C. Cells were pulse labeled with [35S]-methionine for 3 min and subsequently chased with excess cold casamino acids. After 15-min and 40-min incubation, translation was stopped by pouring 1 mL culture over ice. Cell lysis was performed on the ice containing a final concentration of 15 μg/mL lysostaphin. Asterisks mark the major differentially produced proteins. (Right) The same gel as in the phosphorimage, stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue G, to indicate equal loading.