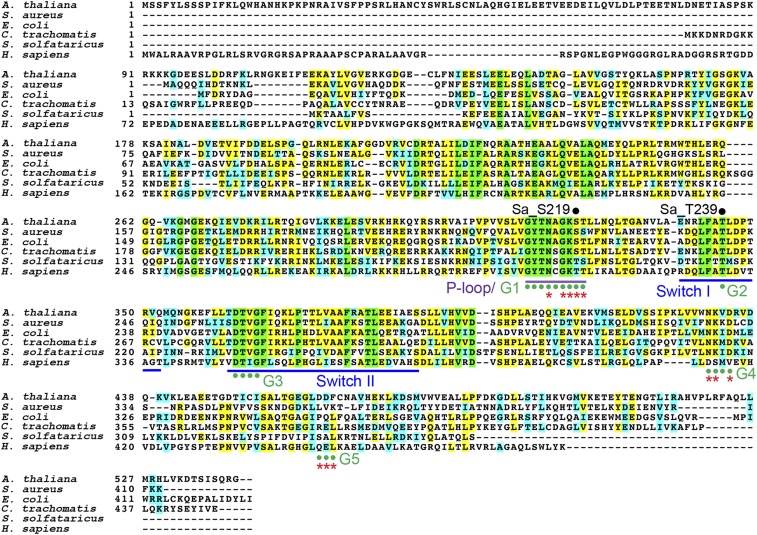
Fig. S1.
Multiple sequence alignment of HflX homologs. HflX homologs are universally conserved from bacteria and plants to humans (33–50% homology). Sequences were extracted from the National Center for Biotechnology Information GenBank with the following accession numbers: Arabidopsis thaliana, AED96978.1; Staphylococcus aureus, ABD21413; Escherichia coli, AAC77130; Chlamydia trachomatis, AAC67975; Sulfolobus solfataricus, AAK40607; and Homo sapiens, O43824 (also known as GTPBP6). Domain structures of P loop, G domains, and Switch I–II regions are color coded. Red asterisks indicate GTP and Mg2+ binding sites. Residues S219 and T239 of S. aureus HflX are labeled.