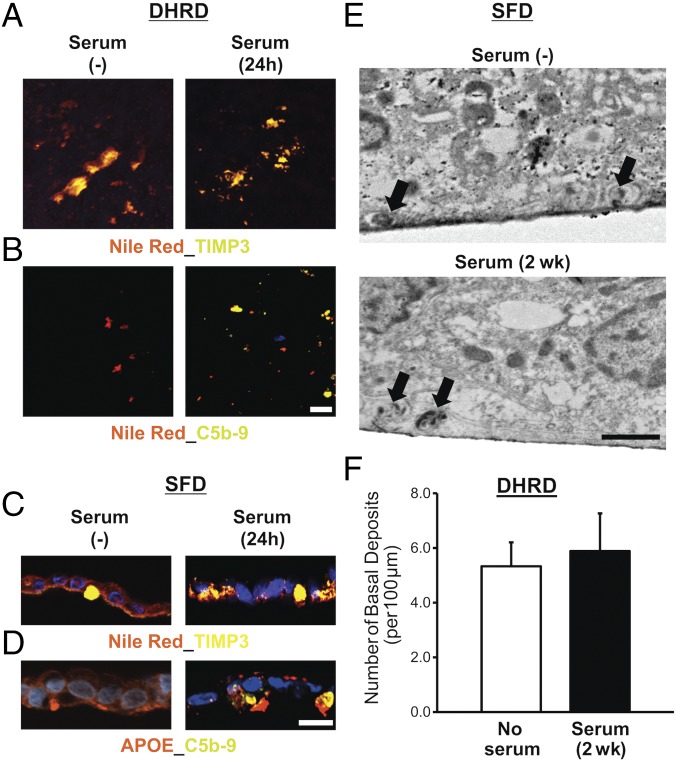
Fig. 7.
Serum supplementation affects the composition of sub-RPE deposits in aged (D90) patient-derived hiPSC-RPE cultures. (A) Confocal microscopy after immunocytochemical analyses showed similar sub-RPE deposition of colocalized neutral lipid–TIMP3 complexes on the surface of Transwell membranes underlying the DHRD hiPSC-RPE (D90) monolayer in untreated vs. serum-treated (10%, 24-h) cultures. (B) Confocal microscopy demonstrated deposition of complement proteins C5b-9 in conjunction with neutral lipids after supplementation of D90 DHRD hiPSC-RPE cultures with 10% serum for 24 h. [Scale bar (applies also to A): 50 µm.] (C) Immunocytochemical analyses of D90 SFD hiPSC-RPE cross-sections after serum supplementation (10%, 24 h) in culture medium demonstrated the presence of Nile red-, TIMP3-positive deposits in both untreated and serum-treated SFD hiPSC-RPE cultures. (D) Immunostaining of D90 SFD hiPSC-RPE cross-sections showed selective deposition of C5b-9 complex with APOE-positive sub-RPE deposits in serum-treated (10%, 24 h) compared with untreated SFD hiPSC-RPE cultures. (E and F) Electron microscopy analyses showed similar numbers of basal deposits (black arrows) in both untreated and serum-treated SFD (E) and DHRD (F) hiPSC-RPE cultures after chronic serum supplementation (10%, 2 wk). Data are presented as mean + SEM. (Scale bar in E: 1 µm.)