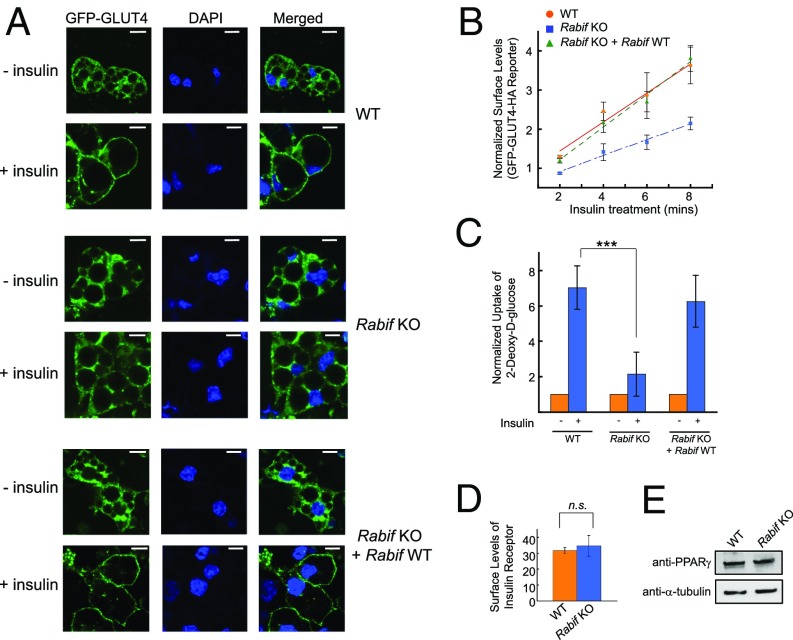
Fig. 2.
RABIF plays a critical role in insulin-stimulated GLUT4 exocytosis. (A) WT or Rabif-KO adipocytes were either untreated or treated with 100 nM insulin for 30 min before the localization of the GLUT4 reporter was visualized by confocal microscopy. (Scale bars: 10 µm.) (B) Normalized surface levels of the GLUT4 reporter in WT or mutant adipocytes. After serum starvation, the cells were treated with 200 µM dynasore for 5 min at 37 °C before 100 nM insulin was added. The cells were harvested for analysis at the indicated time points. Error bars indicate SD. (C) Normalized 2-deoxy-d-glucose uptake into WT or mutant adipocytes. ***P < 0.001. Error bars indicate SEM from four independent experiments. (D) Normalized surface levels of insulin receptor in WT or mutant adipocytes. n.s., not significant. (E) Immunoblots showing the expression levels of PPARγ and α-tubulin in WT or mutant adipocytes.