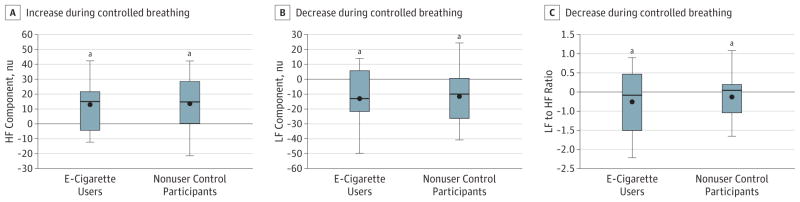
Figure 2. Heart Rate Variability During Controlled Breathing.
A, Within each group (e-cigarette users and nonuser control participants), the high-frequency (HF) component was significantly increased during controlled breathing compared with spontaneous breathing. Similarly, within each group, the low frequency (LF) (B), and LF to HF ratio (C) were decreased during controlled compared with spontaneous breathing, consistent with a relative increase in cardiac vagal and decline in cardiac sympathetic influence. However, between e-cigarette user and nonuser groups, the magnitude of the increase in HF and decrease in LF and LF to HF ratio during controlled breathing were not different.
aP = .05, within-group difference between controlled breathing and spontaneous breathing.