Figure 1.
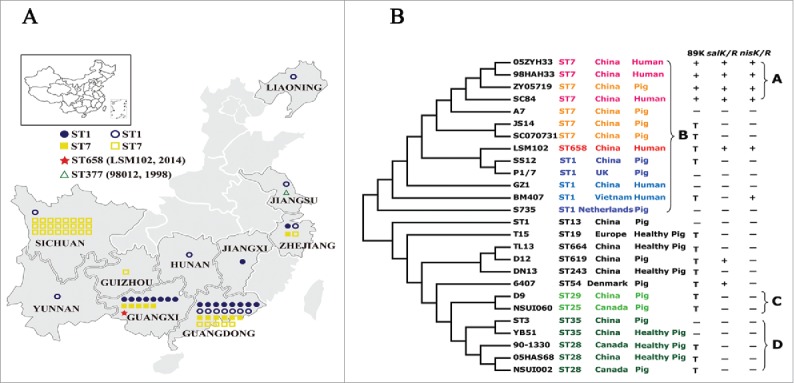
(A) Geographic distribution and sequence types of human S. suis isolates from 2006-2016 in this study. One symbol represents an isolate. Closed symbols denote isolates collected in this study, and open symbols denote isolates reported by literatures or MLST database. (B) The phylogeny of 26 completely sequenced S. suis strains. The Maximum likelihood tree was estimated by the SNPs of a core genome contained 885 genes. Bootstrapping was conducted using 500 replicates. The SC84 strain of S. suis was used as a reference. The label of each branch orderly showed the sequence type, the country and the host from which the S. suis strain was obtained. Then it marks whether or not the strain harbors the 89K PAI, salKR or nisKR (+ : the complete 89K PAI is included, salKR or nisKR; − : the complete 89K PAI is absent, salKR or nisKR; T : partial of 89K PAI associated region is detected).
