Figure 2.
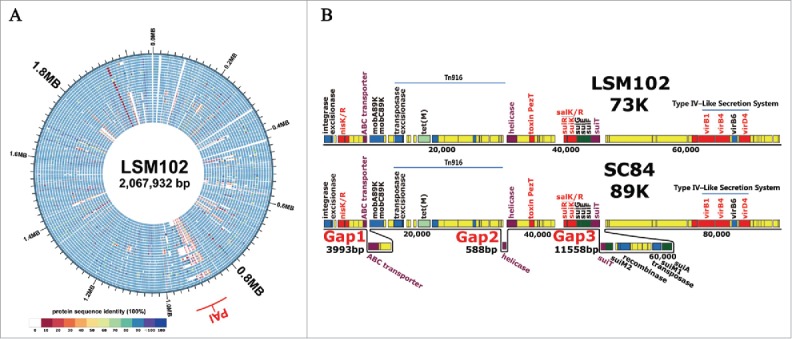
(A) Genomic comparison of 26 S. suis genomes. The circular diagrams showed the variations of LSM102 compared with the other completely sequenced S. suis strains. From outside to the inside, the order of the genomes was: LSM102, SS12, P1/7, ZY05719, SC84, 98HAH33, 05ZYH33, A7, SC070731, JS14, GZ1, BM407, S735, ST1, TL13, D12, DN13, T15, 6407, NSUI060, D9, NSUI002, 05HAS68, 90-1330, YB51, ST3. The different colors stand for the percentage of protein sequence identity. (B), Gene organization of 73 kb pathogenicity island (73K PAI) of LSM102. Virulence-related factors including SalKR, NisKR and Type IV–Like Secretion System (VirD4, VirB1, VirB4) that have been reported to be involved in full virulence of STSS-causing Chinese S. suis were included in 73K PAI of LSM102. Compared with 89K, 3 fragment losses/deletions occur in 73K PAI of LSM102, which were designated as Gap1, Gap2, and Gap3 respectively.
