Figure 5.
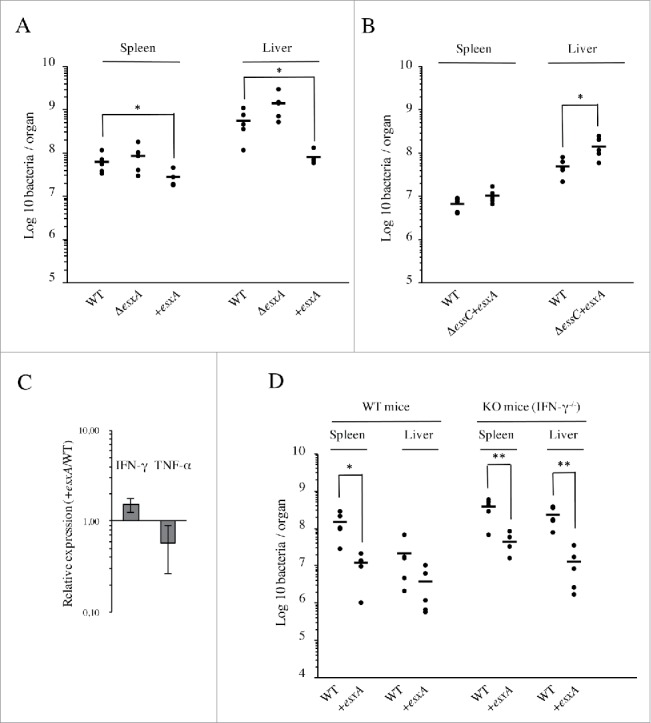
EsxA secretion impairs Lm infection in vivo through an IFN-γ-independent mechanism. (A) Bacterial counts for WT, ΔesxA and +esxA strains, in spleens and livers of BALB/c mice (n = 5), 72h after intravenous infection with 104 bacteria. (B) Bacterial counts for WT and ΔessC+esxA strains, in spleens and livers of BALB/c mice (n = 5), 72h after intravenous infection with 104 bacteria. (C) Levels of IFN-γ and TNF-α transcripts measured by qRT-PCR in livers of mice 72h after intravenous infection with either WT or +esxA bacteria. Expression levels in +esxA-infected livers were normalized to those infected with the WT strain. Values are mean ± SD (n = 3). (D) Bacterial counts for WT and +esxA strains in spleens and livers of WT and IFN-γ knock-out mice (n = 5), 72h after intravenous infection with 104 bacteria. *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01.
