Figure 4.
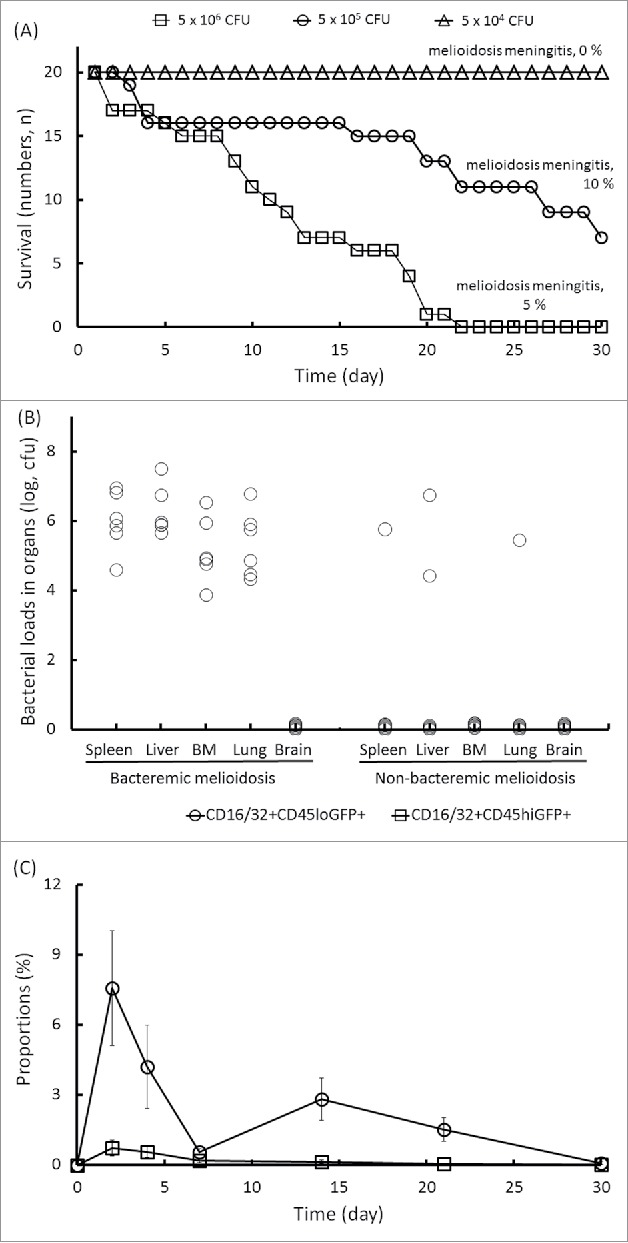
Manifestation of melioidosis in C57BL/6 mice. C57BL/6 mice were intravenously infected with 5 × 104, 5 × 105 and 5 × 106 CFU of B. pseudomallei GFP. During a 30-d infection, the daily survival rates were recorded, and the percentages of mice with neurologic melioidosis at the end of the experiment were confirmed by histological brain examination (A). In the infective doses of 5 × 105 CFU of B. pseudomallei GFP, the bacterial loads in the organs (n = 6; spleen, liver, lung, BM and brain) for melioidosis with bacteremia or non-bacteremia on d 14 post-infection are shown (B). The changes in the numbers of circulating CD16/32+CD45hiGFP+ cells and resident CD16/32+CD45loGFP+ cells in the brain-infiltrating leukocytes during melioidosis are shown (C).
