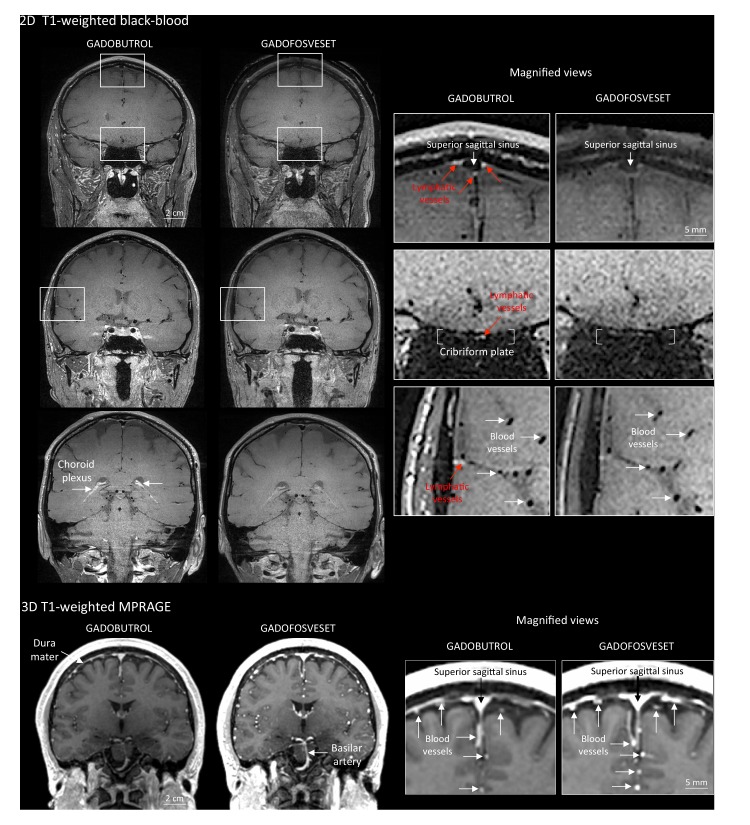
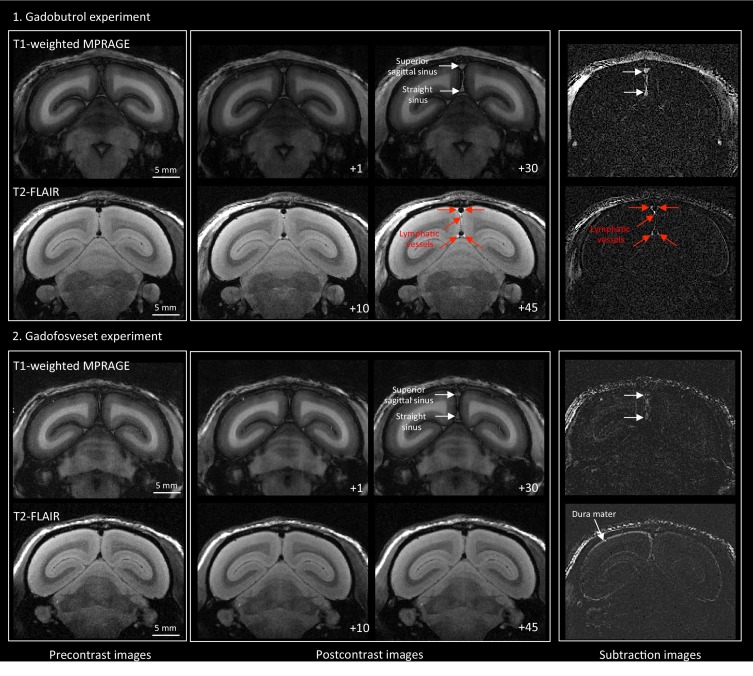
Figure 2. Gadobutrol vs. gadofosveset in MRI-visualization of dural lymphatic vessels.
Coronal T1-weighted black-blood images were acquired after intravenous injection of two different gadolinium-based contrast agents (31 min after gadobutrol and 42 min after gadofosveset), during two MRI sessions separated by one week. Dural lymphatics (red arrows in magnified view boxes) were better discerned using gadobutrol (standard MRI contrast agent, which readily enters the dura) compared to gadofosveset (serum albumin-binding contrast agent, which remains largely intravascular) and were localized around dural sinuses, middle meningeal artery, and cribriform plate (white arrows). Notably, the choroid plexus (white arrows) enhanced less with gadofosveset than gadobutrol, whereas meningeal and parenchymal blood vessels (both veins and arteries) did not enhance with any contrast agent and appeared black. On conventional T1-weighted MPRAGE images, meningeal and parenchymal blood vessels enhanced with both contrast agents, more clearly with gadofosveset.