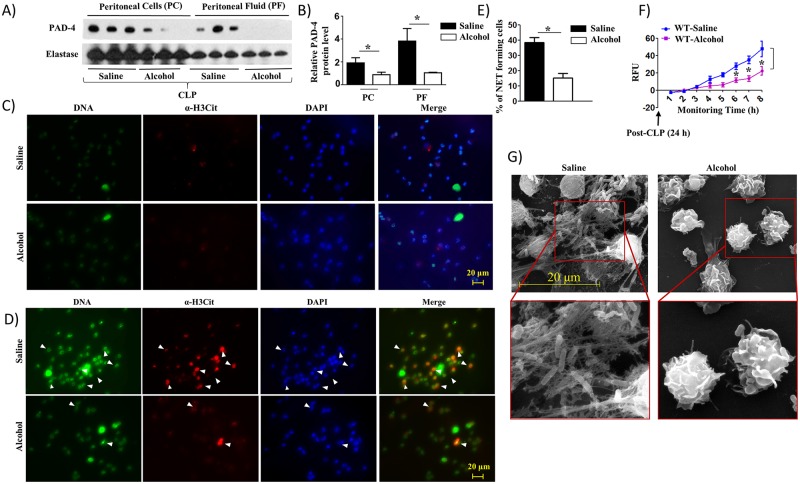
Fig 2. Alcohol impairs NETosis in response to CLP.
A, Western blot of PAD-4 and neutrophil elastase expression in peritoneal cells (neutrophils) and peritoneal fluid from alcohol-administered and control (saline-challenged) mice at 24 h post-CLP. n = 3 mice/group from two independent experiments. B. Relative band densities normalized against neutrophil elastase are representative of the blots. C-D, Peritoneal cells (neutrophils) harvested from alcohol-challenged and control (saline-challenged) mice at 24 h post-CLP were washed with saline (0 h), added SYTOX Green and allowed to monitor NETosis for 8 h and then were fixed. Neutrophils were stained with DAPI to stain DNA and citrullinated H3 Ab (α-H3Cit) to visualize citrullinated histone. Double-positive cells are indicated by arrowheads as evidence of NETosis. Images presented are representative of two independent experiments (n = 5-7/group). E, Twenty random images were selected from three experiments and quantified for the presence of double-positive (SYTOX Green and H3Cit) peritoneal cells (neutrophils) from alcohol-administered and control mice. n = 5-8/group. F, Kinetic analysis of NETosis by peritoneal cells (neutrophils) harvested from alcohol-administered and control mice, washed with saline, and NETosis was measured up to 8 h. Relative fluorescence intensity (RFU) was determined to evaluate NETosis each hour up until 8 h of in vitro culture. n = 6-9/group. G, Evaluation of NETosis by SEM. Peritoneal cells (neutrophils) harvested from alcohol-administered and control mice after CLP were analyzed by SEM. Presence of long thread-like structures is evidence of NETosis. Images presented are representative of two independent experiments (n = 5-8/group). *, p<0.05. NET forming peritoneal cells (neutrophils) are indicated by the arrows on merged images and original magnification 20x. SEM original magnification 8000x.