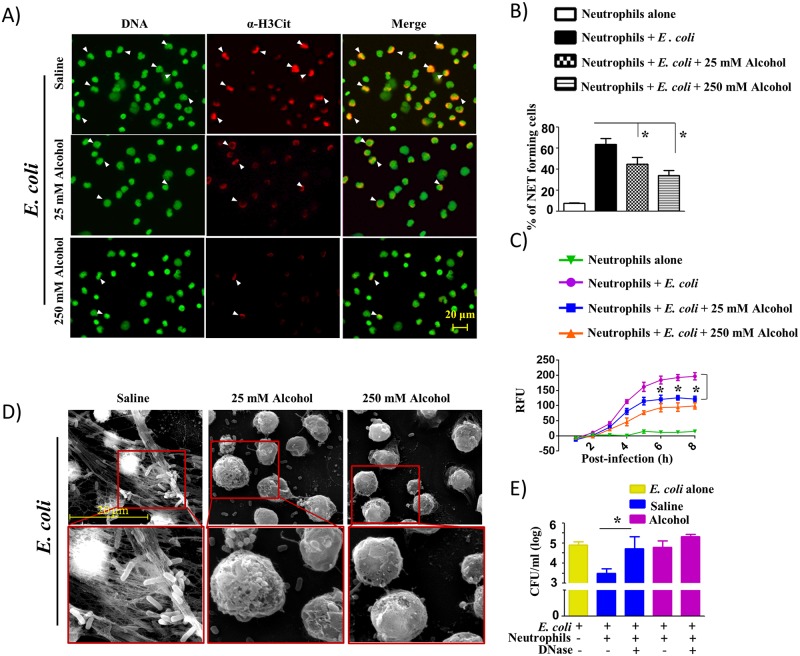
Fig 3. Alcohol reduces NETosis and NET-mediated bacterial killing in mouse bone marrow-derived neutrophils triggered by E. coli infection.
A, Mouse neutrophils harvested from WT mice were pretreated with either 25 or 250 mM alcohol before infection with E. coli (MOI 1), added SYTOX Green, allowed to undergo NETosis, and then fixed after 8 h. Neutrophils were stained with citrullinated H3 Ab to visualize citrullinated histones in fixed cells. DNA and Citrullinated histones are indicated by arrowheads and double positive cells are considered of NETosis. Images presented are representative of three independent experiments (each in duplicate). B, Twenty random images were selected from three experiments and quantified for the presence of NET-positive neutrophils. C, Kinetic analysis of NETosis by E. coli-infected mouse neutrophils treated with alcohol. Mouse neutrophils were pretreated with either 25 mM or 250 mM alcohol and infected with E. coli and stained with SYTOX Green DNA stain to visualize every hour over a period of 8 h. Relative fluorescent intensity (RFU) was determined to evaluate NETosis. Significant differences between infected and alcohol-treated (25 mM alcohol) are indicated by asterisks. D, Evaluation of NETosis by SEM. Mouse neutrophils were pretreated with either 25 or 250 mM alcohol before infection with E. coli and incubation for 8 h to allow for NETosis. E, Alcohol-treated mouse bone marrow neutrophils exhibited diminished NET-mediated killing activity. Bacterial killing capacity of E. coli-infected, alcohol-treated and untreated bone marrow neutrophils was determined by assessing extracellular (CFUs) at 8 h post-infection with E. coli (MOI 1) in the presence or absence of DNase. For experiments A-E, four to five mice/group were used and cells used in triplicate in 3 separate experiments, *, p<0.05. NET forming neutrophils are indicated by the arrows on merged images and original magnification 20x. SEM original magnification 8000x.