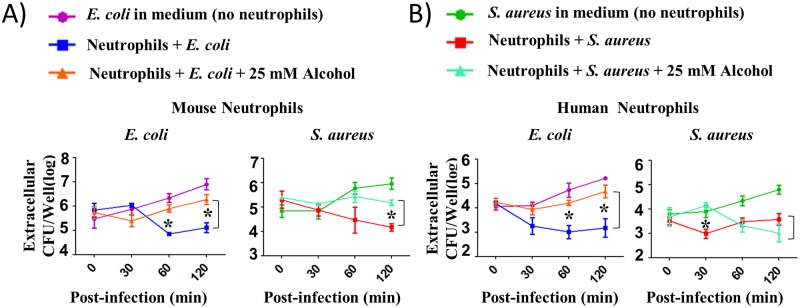
Fig 6. Alcohol impairs extracellular bacterial killing of mouse and human neutrophils.
A-B, Bacterial killing capacity of mouse bone marrow-derived neutrophils (A) and human peripheral blood-derived neutrophils (B) pretreated without or alcohol (25 mM) and infected with an MOI of 1 was determined by assessing extracellular CFUs at 30, 60, and 120 min after infection with E. coli or S. aureus. Experiments were performed in triplicate wells and from three independent experiments and 3–5 mice/group was used. For human neutrophils, 4–5 donors were used per group (*p <0.05 between infected groups in the presence and absence of alcohol).