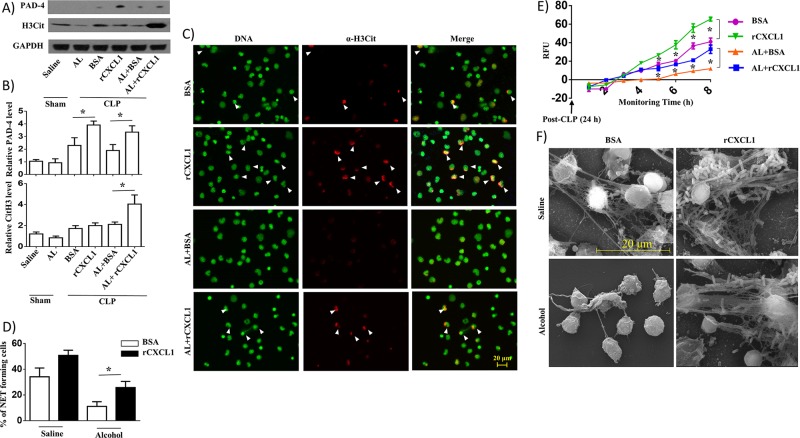
Fig 8. rCXCL1 enhances NETosis in alcohol-challenged septic mice.
A, Western blotting of PAD-4, H3Cit and GAPDH in peritoneal cells (neutrophils) from alcohol-administered and control mice at 24 h post-CLP after rCXCL1 or BSA administration. This blot is representative of three independent experiments with identical results. B. Relative densities normalized against GAPDH are representative of the blots from 3 separate experiments (n = 3-5/mice/group). C, Peritoneal cells (neutrophils) harvested from alcohol-challenged and control mice after CLP were allowed to undergo NETosis after adding SYTOX Green for 8 h and then were fixed. Neutrophils were stained with citrullinated H3 Ab (α-H3Cit) to visualize citrullinated histone. Double-positive cells are indicated by arrowheads as evidence of NETosis. Images presented are representative of three independent experiments (n = 5-7/group). D, Twenty random images were selected from three experiments and quantified for the presence of NET-positive (double-positive; SYTOX Green- and H3Cit-positive) neutrophils from alcohol-administered and control mice. n = 5-8/group. E, Kinetic analysis of NETosis by peritoneal cells (neutrophils) harvested from alcohol-administered and control mice. Relative fluorescence intensity (RFU) was determined to evaluate NETosis each hour up until 8 h of culture. n = 6-9/group. Significance was calculated between rCXCL1 treated and BSA treated peritoneal cells from mice in the presence or absence of alcohol. F, Evaluation of NETosis by SEM. Peritoneal cells (neutrophils) harvested from alcohol-administered and control mice after CLP in rCXCL1 or BSA administration were analyzed by SEM. Presence of long thread-like structures (arrowhead) is evidence of NETosis. Scale bars, 20 μm. (n = 5–8 mice/group); NET forming neutrophils are indicated by the arrows and original magnification 20x; *, p<0.05. AL, alcohol. Arrow indicates NET forming cells on merged images. SEM original magnification 8000x.