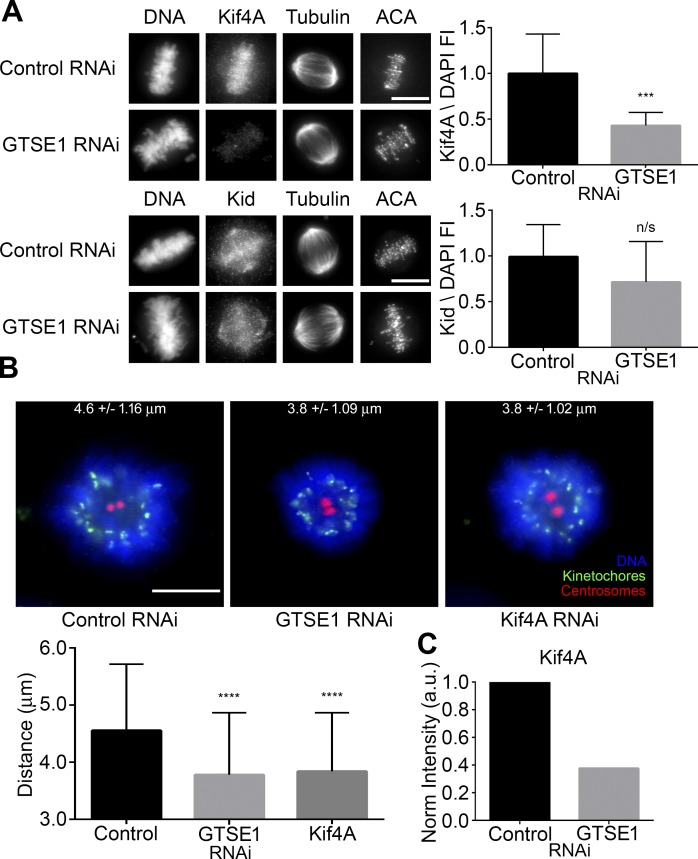
Figure 7.
GTSE1 depletion reduces Kif4A levels on mitotic chromosomes and polar ejection forces in monastrol-treated cells. (A, left) Immunofluorescence of Kif4A or Kid levels in metaphase HeLa cells transfected with either control or GTSE1 siRNA. Cells were coimmunostained for DNA, tubulin, and kinetochores. Images represent maximum-intensity projections. Both Kif4A and Kid levels are scaled equivalently in each panel. (Right) Fluorescence intensity quantification of chromosome-bound Kif4A or Kid after control or GTSE1 siRNA transfection. Depletion of GTSE1 greatly reduced the levels of Kif4A bound to chromatin during metaphase, whereas Kid levels were slightly reduced but not to a significant degree. n = 15 cells from two independent experiments for each condition. FI, fluorescence intensity. (B, top) HeLa cells transfected with either control, GTSE1, or Kif4A siRNA (Wandke et al., 2012; Barisic et al., 2014) were treated with monastrol for 2 h and immunostained for DNA, kinetochores, and centrosomes (γ-tubulin). Numbers indicate mean kinetochore-to-pole distances ± SD of the pooled data from four independent experiments. Control n = 50 cells, GTSE1 n = 40 cells, and Kif4A n = 38. (Bottom) Depletion of either GTSE1 or Kif4A resulted in a significant decrease in the distance between kinetochores and centrosomes, suggesting a reduction in polar ejection forces. SD is plotted for the mean from each condition. Asterisks indicate statistical significance of mean value difference when compared with control as assessed by Kruskal-Wallis test. Bars, 10 µm. ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. (C) Quantification of the chromosome-bound Kif4A fraction from the immunoblot shown in Fig. S3 B. Kif4A levels were normalized to histone H3. Note that the reduction in KIf4A levels by immunoblot was comparable to data obtained by immunofluorescence (A, top) in the absence of GTSE1.