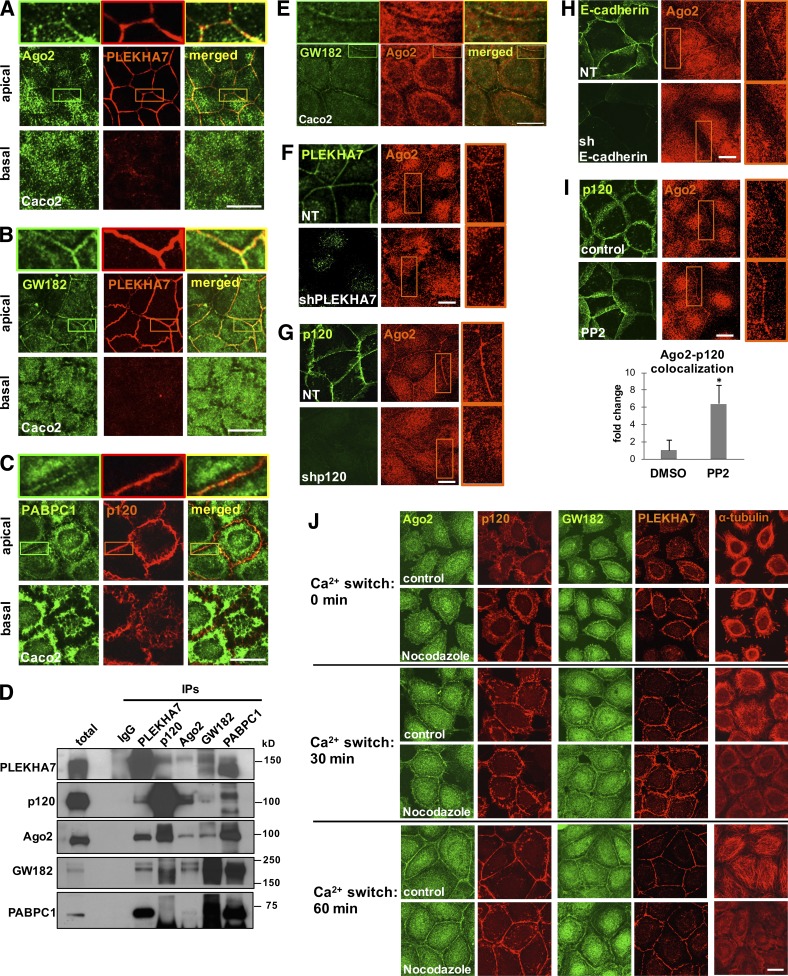
Figure 1.
Cadherin complexes recruit RISC to the apical junctions of polarized epithelial cells. Caco2 cells were grown to polarize and subjected to immunofluorescence for PLEKHA7 or p120 and the core proteins of the RISC complex Ago2 (A), GW182 (B), and PABPC1 (C). Images were obtained by confocal microscopy, and image stacks were acquired across the entire polarized monolayer; representative apical-basal images are shown. Enlarged parts of images on top of each stack indicate areas of cell–cell contact. (D) Western blots of PLEKHA7, p120, Ago2, GW182, and PABPC1 IPs of Caco2 cells for the same markers. IgG is the negative control. Molecular masses (kD) are indicated on the right. (E) Confocal microscopy images after immunofluorescence of Caco2 cells for GW182 and Ago2. Enlarged parts of images on top indicate areas of cell–cell contact. (F) Immunofluorescence of control (nontarget; NT) or PLEKHA7 knockdown (shPLEKHA7) Caco2 cells for Ago2, costained for PLEKHA7. PLEKHA7 background intracellular staining is an artifact of paraformaldehyde fixation. (G) Immunofluorescence of control (NT) or p120 knockdown (shp120) Caco2 cells for Ago2, costained for p120. (H) Immunofluorescence of control (NT) or E-cadherin knockdown (shE-cadherin) Caco2 cells for Ago2, costained for E-cadherin. (I) Caco2 cells treated with either vehicle control (DMSO) or the Src inhibitor PP2 were costained by immunofluorescence for p120 and Ago2. Colocalization of the Ago2 and p120 signals (bottom) was calculated using the Manders coefficient and expressed as fold change of the DMSO control (mean ± SD from n = 3 independent experiments; *, P < 0.02, Student’s two-tailed t test). (J) Calcium switch assay of Caco2 cells for the indicated time points after Ca2+ readdition (Ca2+: 0 min indicates Ca2+ depleted cells immediately before Ca2+ readdition), treated with vehicle (control) or 10 µM nocodazole and stained by immunofluorescence for α-tubulin, PLEKHA7, p120, Ago2, and GW182. Bars, 20 µM. Insets are magnified 3×.