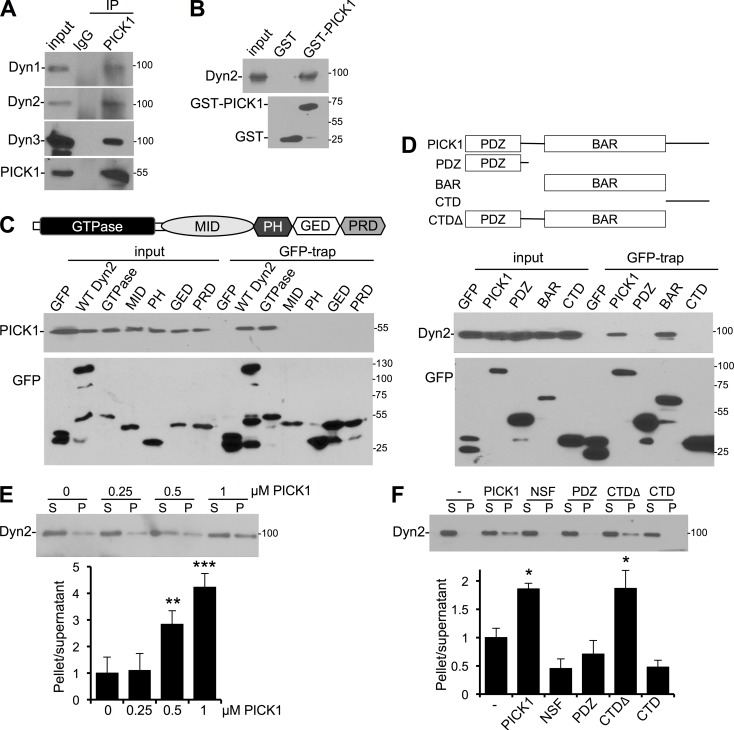
Figure 4.
PICK1 binds dynamin via BAR and GTPase domains and regulates dynamin polymerization. (A) Endogenous PICK1 interacts with endogenous dynamin 1, 2, and 3 in neurons. Extracts of cortical neurons were immunoprecipitated with PICK1 antibody or control IgG. Proteins were detected by Western blotting. Input is 5% of offered protein. Blots shown are representative of more than five independent experiments. (B) PICK1 interacts directly with dynamin. GST or GST-PICK1 was immobilized on glutathione agarose and incubated with purified HA-dynamin. Proteins were detected by Western blotting. Blots shown are representative of four independent experiments. (C) PICK1 interacts with the GTPase domain of dynamin. HEK293 cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing Flag-PICK1 and GFP, GFP–dynamin 2, or dynamin domains as indicated. Cells were lysed and incubated with GFP-trap agarose. Blots shown are representative of five independent experiments. (D) Dynamin interacts with the PICK1 BAR domain. HEK cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing HA-dynamin and GFP, GFP-PICK1, or truncations, as indicated in the top panel. Cells were lysed and incubated with GFP-trap agarose. Blots shown are representative of five independent experiments. (E) PICK1 promotes dynamin polymerization. His6-PICK1 at the concentrations indicated was incubated with HA-dynamin. Polymerized dynamin was pelleted by centrifugation, and protein in the supernatant and pellet was analyzed by Western blotting. Graph shows the ratio of dynamin in pellet/supernatant (n = 4 independent experiments; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test; values are means ± SEMs). (F) HA-dynamin was incubated with his6-PICK1, his6-NSF, or his6-PICK1 truncations as indicated and processed as in E. Graph shows the ratio of dynamin in pellet/supernatant (n = 7 independent experiments; *, P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test; values are means ± SEMs). CTD, C-terminal domain.