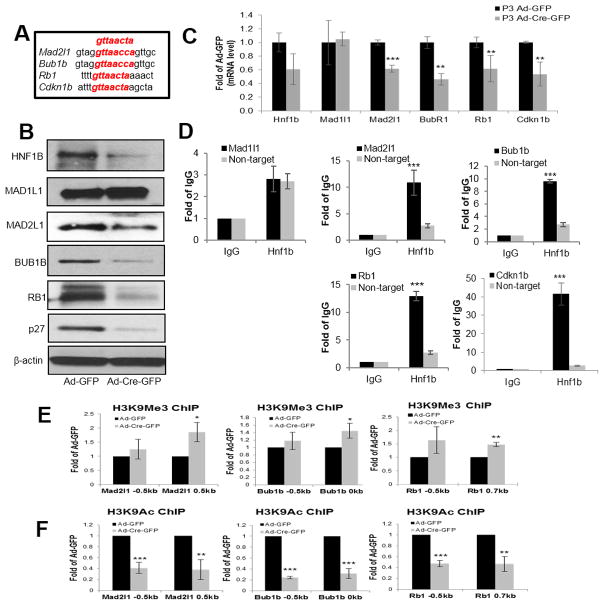
Figure 4. Hnf1b deficiency reduced spindle checkpoint (MAD2L1, BUB1B) and cell cycle checkpoint (RB1, and p27) expression at protein, mRNA levels and affected chromatin access of Mad2l1, Bub1b and Rb1 genes in proliferating MEFs.
Consensus DNA sequence of HNF1B binding aligned with predicted highest score sequences of each substrate (A). Protein levels of HNF1B, MAD1L1, MAD2L1, BUB1B, RB1, p27 and b-actin examined by immunoblotting after Ad-GFP and Ad-Cre-GFP infection for 72 h in P3 primary Hnf1bflox/flox MEFs (B). Relative mRNA levels normalized to Gapdh and determined by qRT-PCR after Ad-GFP and Ad-Cre-GFP infection for 48 h (C). ChIP of HNF1B or IgG against Mad1l1, Mad2l1, Bub1b, Rb1 and Cdkn1b primers based on best postulated binding scores as well as non-targeted primers (D). Chromatin immunoprecipitation of repressing (H3K9me3) (E) and activating (H3K9ac) (F) histone H3 modifications of Mad2l1, Bub1b and Rb1 at two different locations close to transcriptional start site. Data are expressed as mean±SD, N=3, *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.