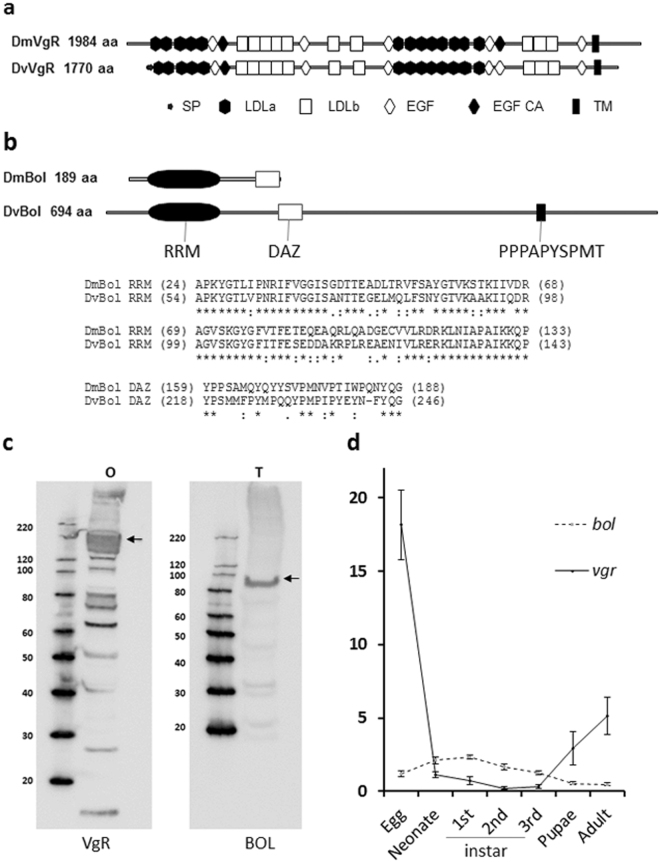
Figure 1.
Predicted protein domains of Diabrotica virgifera virgifera VgR and BOL and expression. (a) VgR protein domain structure. Drosophila (DmVgR) and DvVgR protein structures are compared and the locations of the signal peptide (SP, black arrow), density lipoprotein receptor class A (LDLa, black hexagon), low-density lipoprotein receptor class B (LDLb, open rectangle), epidermal growth factor-like (EGF, open diamond), EGF-like with calcium binding site (EGF CA, black diamond), and transmembrane (black rectangle) domains are indicated. (b) BOL protein domain structure. DmBol and DvBol protein structures are compared and the locations of RNA recognition motif (RRM, black oval), Deleted in Azoospermia (DAZ, open rectangle), and PPPAPYSPMT regions are indicated. Sequence alignments of RRM and DAZ between DmBol and DvBol are shown with indications of identical amino acid (*), high similarity (:), and weak similarity (.) amino acids. The numbers in parenthesis show the beginning and ending positions of amino acids in the BOL proteins. (c) Western blot detection of VgR and BOL proteins in D. virgifera virgifera adult reproductive tissues. Proteins were extracted from the dissected ovary and testes using different methods, as described in the Supplementary method A. Loaded samples represent the equivalent of 1 ovary (O) or 2.5 testes (T), based on optimized conditions (Supplementary Fig. 2). VgR and BOL were detected using polyclonal peptide antibodies and protein size was estimated using a standard marker. Full-length blots are presented in the Supplementary Fig. 2c. (d) Relative mRNA expression of D. virgifera virgifera target genes in different life stages. qRT-PCR was used to examine gene expression of vgr and bol after feeding on diet incorporated with 50 ng μl−1 or different doses of vgr and bol fragment dsRNA. Relative expression analysis (mean ± SE) was based on bol and vgr expression in individual insects (n = 12) at each life stage, after being normalized to the expression of the reference gene, dvrps10.