Fig. 2.
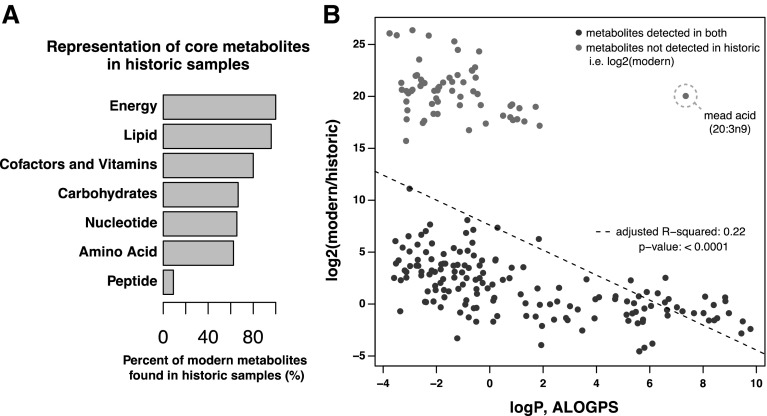
Compound preservation is correlated with aqueous solubility. a Percent of high ubiquity metabolites in modern calculus that were also recovered in at least one historic calculus sample. Peptides exhibit the poorest representation in historic dental calculus, with only 9% of the peptides observed to be present in all five modern calculus samples also detected in any historic sample. By contrast, Lipids and Energy (TCA cycle) super-pathways exhibit high representation in historic calculus, with > 96% of compounds found in all five modern samples also recovered from historic dental calculus. Xenobiotics, which largely comprise dietary and pharmaceutical compounds, are not shown. b The log2 fold-change (modern/historic) of metabolite abundance versus the 1-octanol versus water partition coefficient (logP), estimated with the ALOGPS tool. In the cases where metabolites were only detected in modern calculus, the log2 values (not fold-change) were plotted relative to logP. The fitted linear model showed a significant effect (p < 0.0001) of logP on metabolite fold-change with and adjusted R2 of 0.22. The outlier from this trend was mead acid (20:3n9)