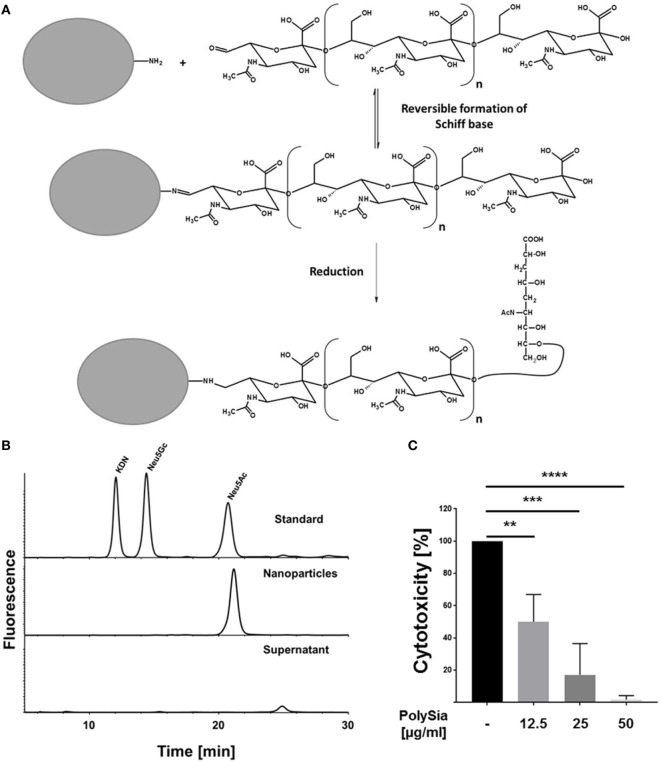
Figure 4.
Polysialylated nanoparticles counteract histone-mediated cytotoxicity. (A) Illustration of the chemical polysialylation on amino modified particles. (B) The sialidases sensitivity of the oxidized polySia chains on nanoparticles were tested using bacterial sialidases. After enzymatic treatment, beads were centrifuged and supernatant as well as the bead-pellet were checked for the presence of Neu5Ac by DMB-HPLC analysis. A sialic acid standard panel (KDN, Neu5GC, and Neu5Ac) was used to determine the retention time of Neu5Ac. (C) In addition, polysialylated nanoparticles were tested for their capability to compensate histone-mediated cytotoxicity. Cells were treated with histones (60 µg/ml) and the cytotoxicity was determined. In parallel, the cytotoxicity was determined in the presence of different concentration of polysialylated nanoparticles. 100% cytotoxicity was set for histone-treated cells. All values are means of three independent experiments. The statistical evaluation was performed by one-way analysis of variance analysis. ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.