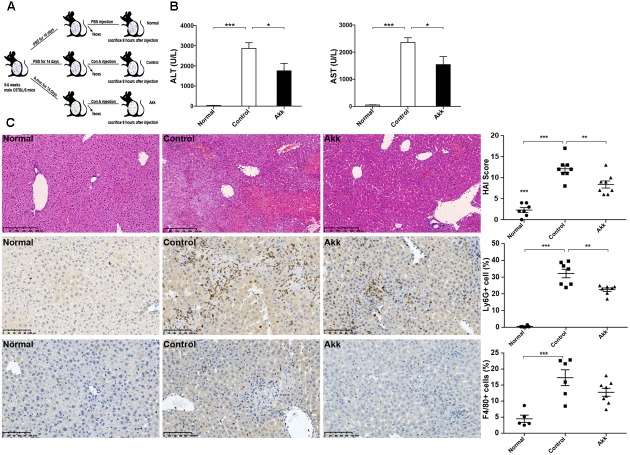
FIGURE 1.
Akkermansia muciniphila administration inhibited Con A-induced acute liver injury. (A) Design of the animal experiment. Mice were randomly distributed to three groups (Normal, n = 8; Control, n = 7; Akk, n = 7). Mice were pretreated with PBS or A. muciniphila continuously for 14 days by gavage. On day 15, feces from each mouse were collected, and Con A was injected. Eight hours later, mice were sacrificed. (B) Serum levels of ALT and AST (n = 7–8 per group). (C) Representative liver histology. Upper panel: Left, H&E staining, scale bar, 250 μm; Right, modified HAI scores of liver histopathology. Middle panel: Left, staining of neutrophils (Ly6G+), scale bar, 100 μm; Right, percentage of Ly6G+ cells. Lower panel: Left, staining of macrophages (F4/80+), scale bar, 100 μm; Right, percentage of F4/80+ cells. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001 by post hoc ANOVA one-way statistical analysis.