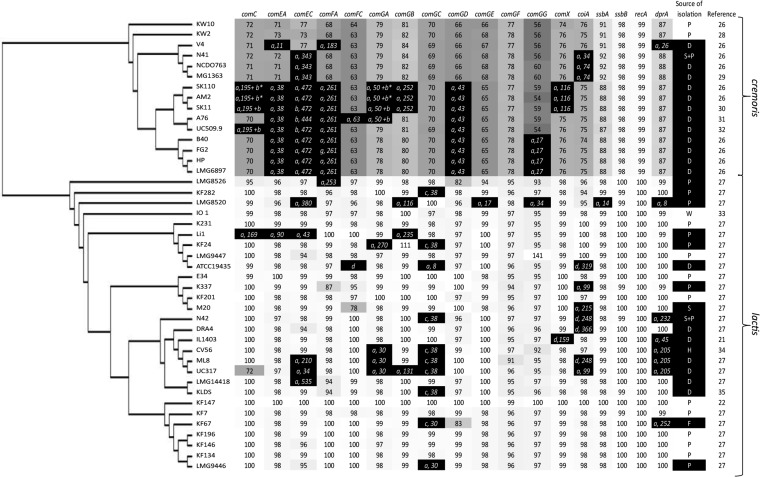
FIG 1.
Genomic analysis of 43 L. lactis strains to assess genetic capacity to develop natural competence. A concatenated core genome single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) tree of 43 L. lactis strain was combined with full-length protein identity scores (%) for the selected subset of late-competence-associated proteins in comparison to their homologues in L. lactis strain KF147, which was used as a reference. Protein identity scores are depicted within each cell and reflected by gray scales based on the L. lactis KF147 query protein sequences, in which at least 90% full-length alignment is considered indicative of gene presence. Genetic events leading to competence gene decay (black cells in the figure) are specified as a premature stop codon within the first 90% of the gene (a), transposon insertion (b), prophage insertion (c), or absence of gene, a mutated/alternative start, or lengthened/fused protein at least more than 25% of its total length (d), followed by the position within the protein sequence where the event is detected relative to its N terminus. Source of isolation: P, plant; D, dairy; S, soil; W, water; H, human body; F, fruit (72). References for the genome sequences are given when available.