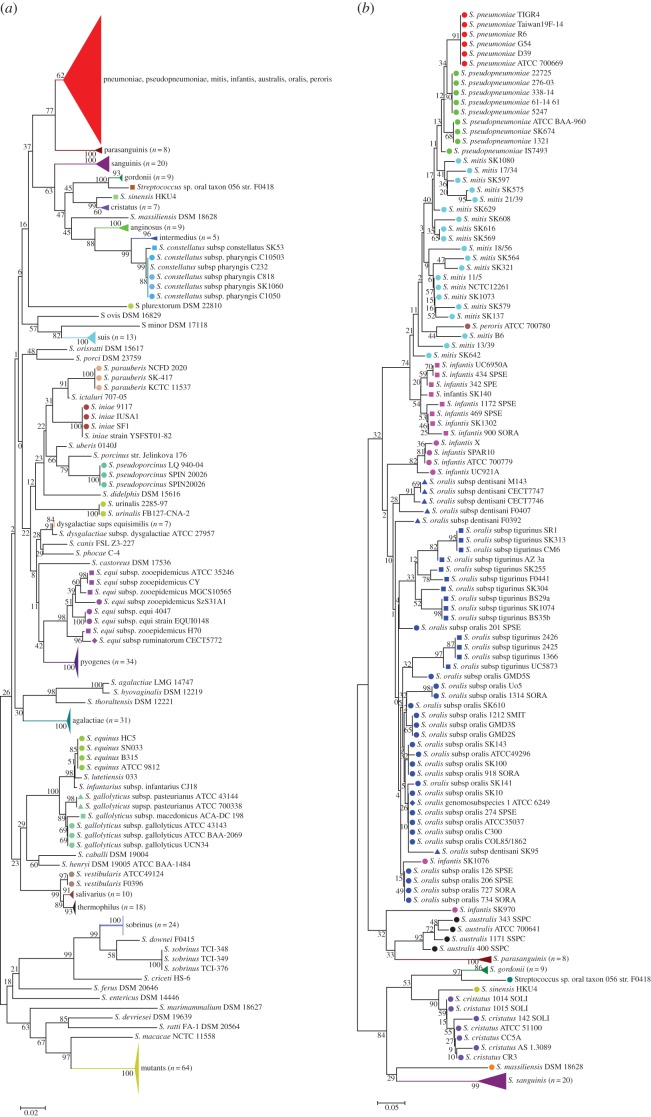
Figure 1.
Cluster analyses of the S2-sequences of (a) the 498 streptococcal strains in the reference dataset (strains of streptococcal species pneumoniae, pseudopneumoniae, mitis, infantis, australis, oralis and peroris are collapsed together, red triangle) and (b) the 360 strains included in the study, belonging to the Mitis group. Phylogenetic analysis was performed using the minimum evolution method with nucleotide substitution type and Maximum Composite Likelihood Substitution Model with bootstrap analysis based on 500 replicates. Strains of the same species are grouped by colour. Different symbols of the same colour indicate subspecies. Magenta squares and circles indicate the two S. infantis clusters identified by Jensen et al. [5] (circles = cluster 1; squares = cluster 2). Different dark blue symbols indicate the different S. oralis subspecies identified by Jensen et al. [5].