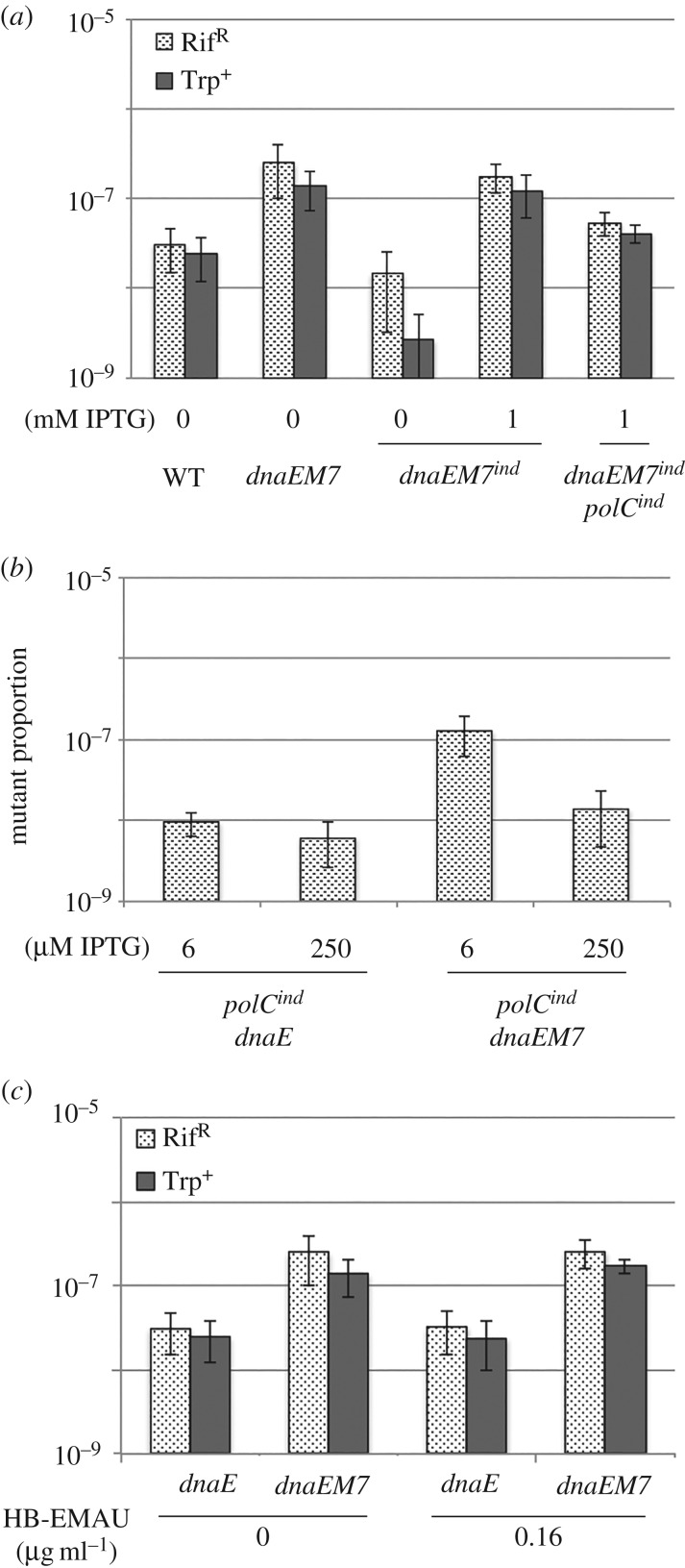
Figure 6.
The rate of DnaE misincorporations inversely correlates with PolC concentration. (a) Mutagenesis in DnaEM7 inducible strains. Isolated colonies of isogenic TrpC− strains encoding DnaEM7 (dnaEM7ind) or DnaEM7 and PolC (dnaEM7ind polCind) from the inducible Pspac promoter were obtained in plates containing 50 µM IPTG. Six independent colonies were then cultivated for about 10 generations in 0 or 1 mM IPTG and plated on 50 µM IPTG to measure the proportion of RifR and Trp+ cells. The mutagenesis rate of the WT and dnaEM7 strains was also determined from six isolated colonies. WT: JJS9; dnaEM7: DGRM850; dnaEM7ind: DGRM838; dnaEM7ind polCind: DGRM848. (b) Effect of PolC depletion on the mutator phenotype of DnaE and DnaEM7. Strains encoding dnaE or dnaEM7 from natural expression signals and polC from the IPTG-dependent Pspac promoter (polCind) were grown in LB plates with 250 µM IPTG. Six independent colonies were then cultivated over a day to carry out about 15 generations at 6 or 250 µM IPTG (note that cell growth ceased at ≤3 µM IPTG). The proportion of RifR cells was determined from freshly saturating cultures. polCind dnaE (DGRM840); polCind dnaEM7 (DGRM841). (c) Effect of HB-EMAU on DnaE and DnaEM7 mutagenesis. Cells encoding DnaE or DnaEM7 from natural expression signals were streaked on LB plates. Six isolated colonies were then grown in the presence or absence of 0.16 µg ml−1 HB-EMAU. At saturation, cells were plated to determine the proportion of RifR and Trp+ mutants. Similar results were obtained at 0.3 µg ml−1 HB-EMAU. WT: JJS9; dnaEM7: DGRM850.