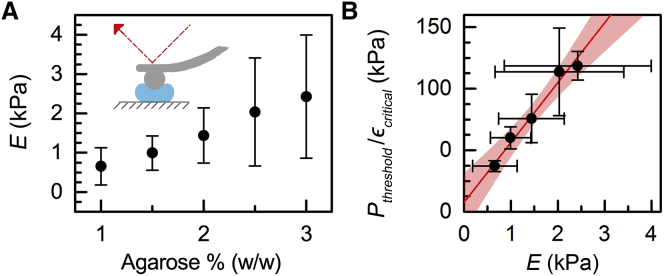
Figure 2.
Stress calibration using agarose gel particles. (A) Elastic moduli of gel particles made with varying concentrations of agarose from 1.0 to 3.0 % (w/w) as measured by AFM. Data represent the average ± SD for N = 12–53 particles over two independent experiments. (B) Agarose calibration particles are used to determine the applied stresses in the q-DC device by measuring the minimum threshold pressure, Pthreshold, required to induce a critical strain, ϵcritical, for a particle to deform through a constricted channel. Shown here are representative data for N > 140 particles transiting through a 5 × 5 μm channel. Horizontal error bars represent the standard deviation of the elastic modulus, as indicated by the vertical error bars in (A). Vertical error bars represent the standard deviation of the threshold-pressure/particle-strain ratio. The line is the linear fit determined by the Deming method. The shaded region illustrates the 95% confidence interval of the fit. The inverse of the slope characterizes the calibration factor, A. To see this figure in color, go online.