Fig. 1.
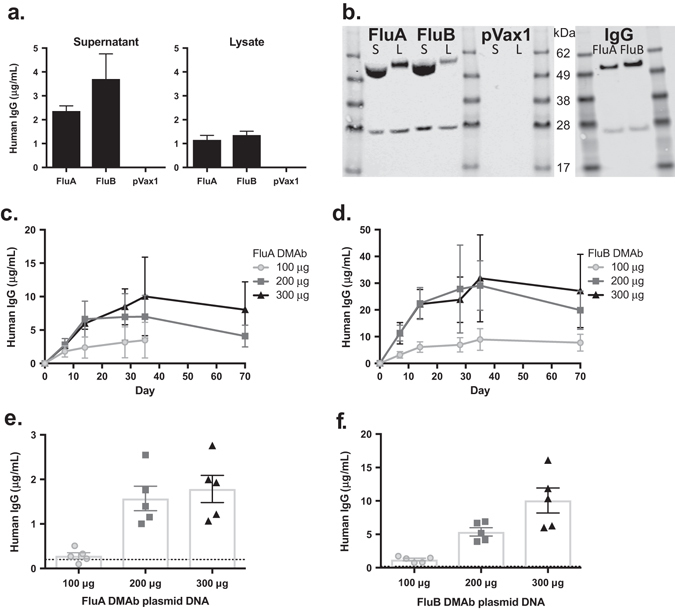
In vitro and in vivo expression of DNA-encoded monoclonal antibody (DMAb) constructs. a 293 T cells were transfected with FluA or FluB DMAb plasmid constructs, or empty plasmid (pVax1). Human IgG expression in cell supernatants (left) and lysates (right) was quantified by ELISA. (n = 3 biological replicates, mean ± SEM). b Western blot of human IgG heavy-chain and light-chain peptides in reduced DMAb-transfected 293 T cell supernatants (S) and lysates (L) (left), and purified protein monoclonal antibody FluA and FluB (IgG, right). Samples derive from the same experiment and gels/blots were processed in parallel. c, d DMAb human IgG in CAnN.Cg-Foxn1 nu/Crl nude mouse sera after intramuscular electroporation (IM-EP) (Day 0) with 100–300 μg of FluA (c) or FluB (d) DMAb plasmid DNA. Sera were collected up to 35 days post electroporation in mice treated with 100 μg FluA DMAb, and up to 70 days in all other groups. (n = 5 animals per group, mean ± SEM). e, f Levels of DMAb human IgG in BALB/c mouse sera 5 days post administration of 100–300 μg of FluA (e) or FluB (f) DMAb plasmid DNA. Dotted line indicates limit of detection (LOD). (n = 5 animals per group, mean ± SEM)
