Figure 1. IL-23R-Dependent Inflammatory Th17 Cells Are Integrin β3hi.
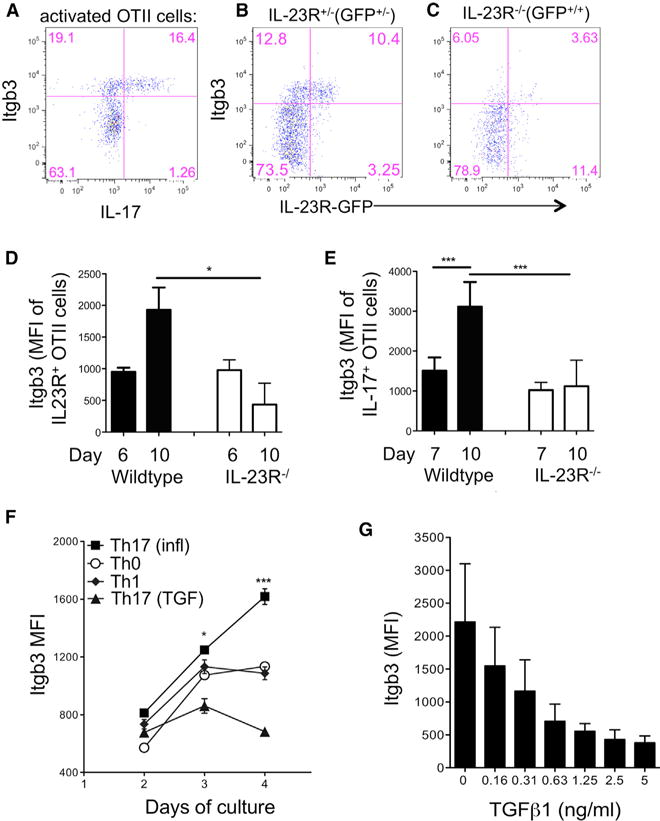
CD4+ T cells from CD45.1+ IL-23R−/− GFP, IL-23R+/− GFP or WT OTII mice were adoptively transferred into WT B6 recipients that were immunized the following day with OVA(323–339) in CFA.
(A) dLN cells were stimulated with PMA/ionomycin on day 10 and OTII cells analyzed by flow cytometry for co-expression of IL-17 and integrin β3, gating on CD4+CD45.1+ cells.
(B) Integrin β3 expression on unstimulated IL-23R+/− GFP+/− CD45.1+ OTII cells taken from dLNs on day 10.
(C) Integrin β3 expression on IL-23R-deficient (IL-23R−/− GFP+/+) CD45.1+ OTII cells taken from dLNs on day 10.
(D and E) Pooled data for integrin β3 expression on wild-type and IL-23R−/− cells as described above, gating on unstimulated IL-23R(GFP)+ OTII cells (D) and IL-17+OTII cells following PMA/ionomycin stimulation (E).
(F) CD4+ T cells from B6 mice were activated with plate-bound anti-CD3 under the following conditions: IL-23, IL-6, IL-1 (Th17(i)), TGF-β + IL-23, IL-6, IL-1 (Th17(TGF)), IL-12 (Th1), or no cytokines (Th0), and expression of integrin β3 was assessed by flow cytometry on indicated days of culture.
(G) Expression of integrin β3 on CD4+ cells cultured in the presence of IL-23, IL-6, and IL-1 with indicated concentrations of TGF-β, analyzed by flow cytometry on day 4.
Data are representative of three separate experiments with four mice per group (A–E) or performed in triplicate (F and G). Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA. Error bars indicate mean ± SD.
