Fig. 4.
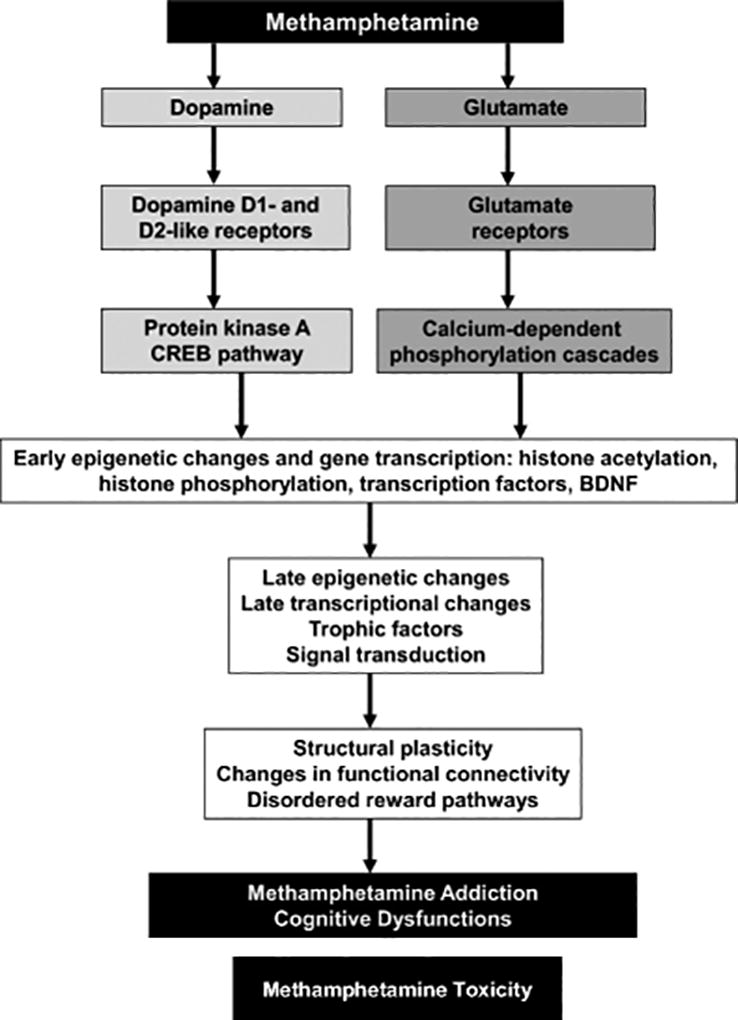
Transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms are involved in METH addiction and toxicity. Biochemical and behavioral effects of METH include activation of dopaminergic and glutamatergic pathways together with other neurotransmitter systems that might participate in the development of addiction and toxicity. Activation of these neurotransmitter systems is followed by activation or inhibition of transcriptional and epigenetic events that underlie compulsive abuse of the drug. These behaviors might be secondary to subcortical hyperconnection syndrome caused by cortical disinhibition and specific cognitive changes in human METH addicts.
