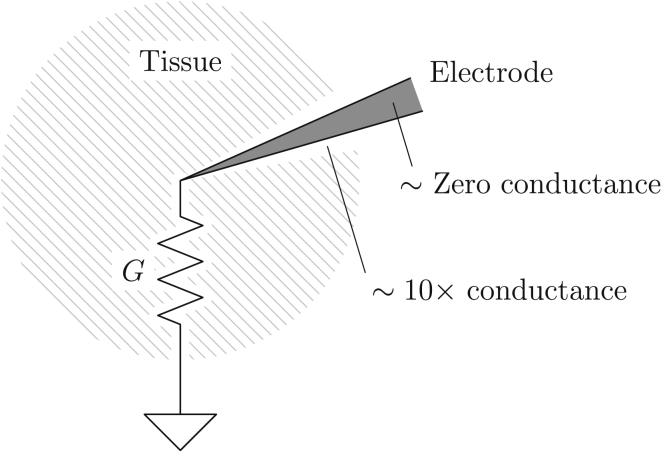
Figure 1.
Diagram for understanding the effect of an electrode on the measurement of the extracellular impedance G. A thin layer around the electrode will exhibit increased conductance, while the electrode itself will have essentially zero conductance, by virtue of its connection to a high-impedance amplifier. For an electrode-affected cone with a generous plane angle of 20° (as drawn), the solid angle it subtends at the electrode would be 0.1 steradians, or less than 1% of 4π.