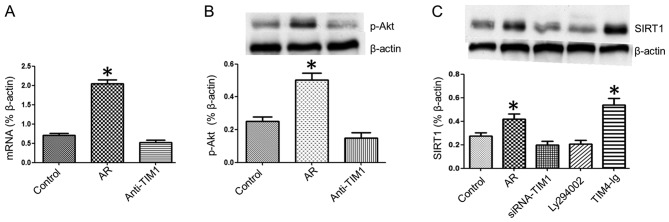
Figure 3.
T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain (TIM)4/TIM1 interaction increases silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) expression in splenic CD4+ T cells. The RNA expression of SIRT1 in the nasal mucosa was evaluated by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Splenic mononuclear cells in each group were collected and cultured with ovalbumin (10 ng/ml) for 3 days. CD4+ T cells were isolated by microbeads and SIRT1 expression was assessed by western blot analysis. (A) The bars indicate the SIRT1 mRNA levels in the nasal mucosa. (B and C) The immune blots show the levels of (B) phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) and (C) the SIRT1 protein in splenic CD4+ T cells. The groups were annotated below the graphs. The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. *P<0.05 vs. the control group. Ly294002, phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt inhibitor; AR, allergic rhinitis.