Fig 1. Schematic of five rat surgical groups used in this study.
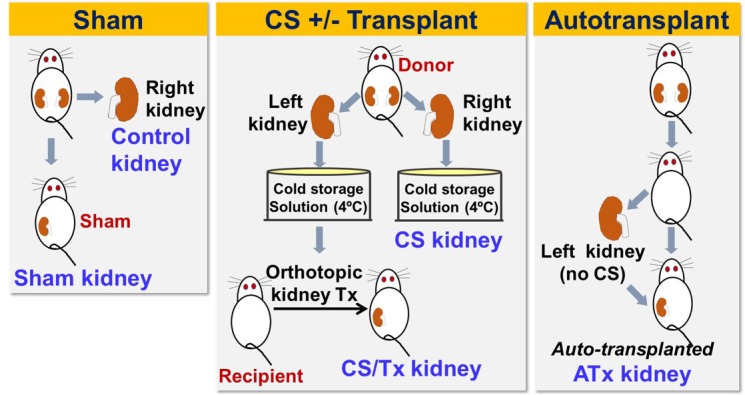
The left panel depicts the sham surgery, in which the right kidney was removed (control kidney) and the rat survives with only the left native kidney (sham kidney). The middle panel shows transplant surgery using donor kidneys (left and right), which were harvested and exposed to cold storage solution for 18 hrs. The right kidney was saved as CS control (CS kidney) and the left kidney was transplanted in a new recipient rat, in which both native kidneys were removed so that the kidney function depends on the transplanted donor kidney (CS/Tx kidney). The right panel shows autotransplant surgery, in which both native kidneys were removed in a rat, but the left native kidney was transplanted immediately back to the same rat. This kidney was saved as autotransplanted kidney (ATx kidney) and served as a control transplant kidney without CS for the CS/Tx kidney.
