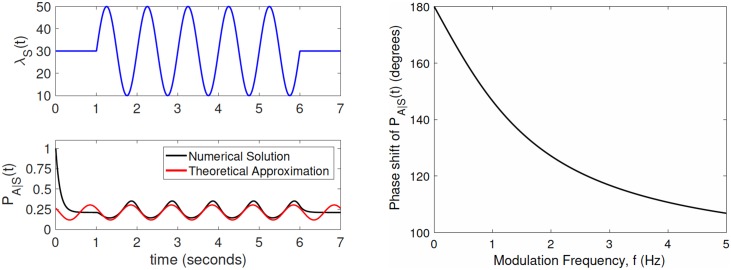
Fig 5. Theoretical calculations of phase shift.
The lower left panel shows that for a modulation frequency of f = 1 Hz, our mathematical derivation of an approximate steady state solution to Eq (10) correctly obtains the phase shift in the conditional vesicle availability probability, PA|S(t), relative to periodic input spike rate modulation, λS(t). In the legend, ‘Theoretical’ corresponds to Eq (12). Parameter values are as shown in Table 3. The right-side panel is shown to make it clear that there is a large phase shift relative to the input stimulation. The phase shift according to a numerical integration of Eq (21) is 144.54° for the numerical solution and 146.52° for the theoretical solutions. The right panel shows the theoretically calculated phase shift (Eq (13)) of conditional vesicle availability probability, PA|S(t). The phase shift is relative to periodic input spike rate modulation, λS(t), as a function of modulation frequency, f.