Figure 5.
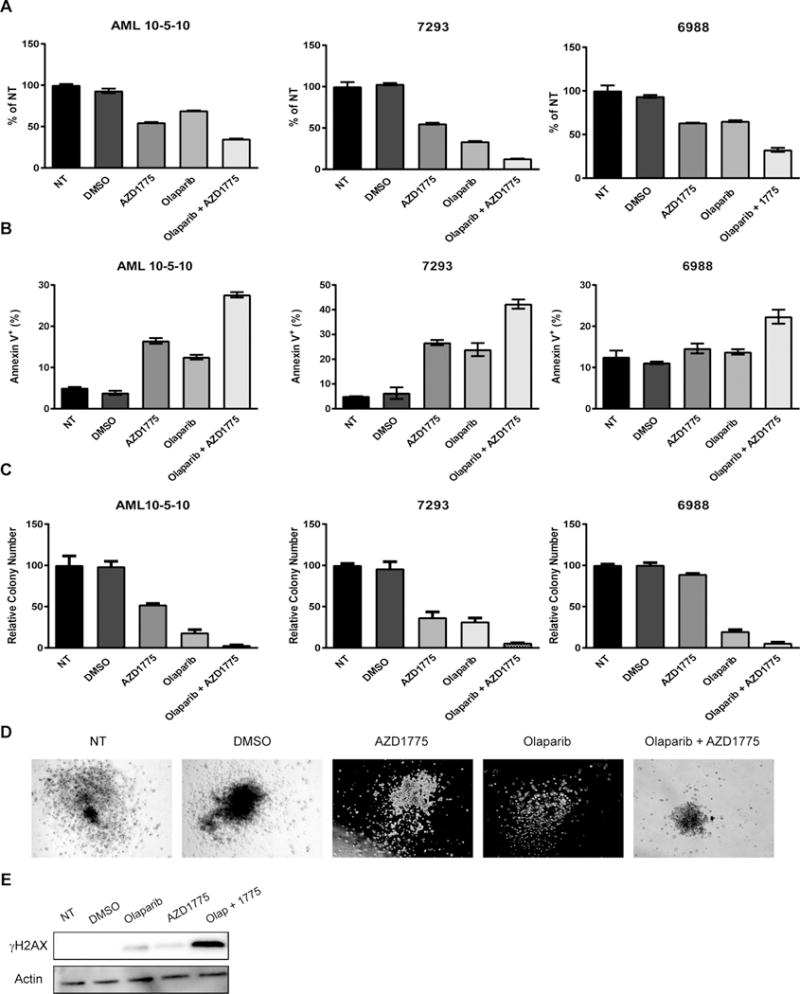
AZD1775 and olaparib reduce proliferation and colony formation and induce apoptosis in AML patient samples. A and B. AML patient samples were treated with DMSO (vehicle control), olaparib (2 uM), and/or AZD1775 (200 nM) for 72 hr and analyzed for cell viability (A) and apoptosis induction (B). Results are displayed as mean ± SEM of two technical replicates. C. Quantification of colonies formed in methylcellulose after continuous exposure to DMSO (vehicle control), olaparib (2 uM), and/or AZD1775 (200 nM) for 10–14 days. Results are normalized to cells receiving no treatment (NT) and are displayed as mean ± SEM of three technical replicates. D. Representative images of AML sample 7293 colonies formed after 10 days of continuous exposure to DMSO (vehicle control), olaparib (2 uM), and/or AZD1775 (200 nM). E. Patient sample AML 10-5-10 was treated with DMSO (vehicle control), olaparib (2 uM), and/or AZD1775 (nM) for 48 hr after which protein lysates were subjected to western blotting using antibodies specific to γH2AX and actin.
