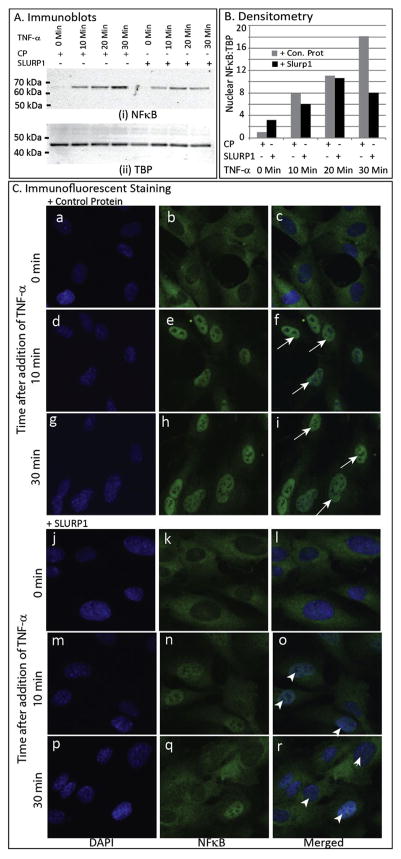
Fig. 7.
Effect of SLURP1 on TNF-α-induced nuclear localization of NFκB in HUVEC cells. (A) Immunoblots with HUVEC nuclear extracts (blots probed with anti-NFκB and anti-TBP antibody). HUVEC cells were pre-treated with control protein or SLURP1 for 30 min, exposed to TNF-α, nuclear extract prepared at 0, 10, 20 and 30 min after TNF-α treatment, separated by SDS-PAGE, and NFκB and TBP detected by immunoblots as indicated. (B) Relative quantities of nuclear NFκB estimated by densitometric scans. NFκB and TBP band intensities were quantified by densitometric scans and NFκB:TBP ratios plotted. (C) Immunofluorescent Staining for NFκB. HUVEC cells were pre-treated with control protein (a–i) or SLURP1 (j–r) for 30 min, exposed to TNF-α, fixed at 0,10, and 30 min after TNF-α treatment, and the sub-cellular localization of NFκB detected by immunofluorescent staining (green). Nuclei are stained blue with DAPI (blue). TNF-α induced nuclear localization of NFκB in control protein treated HUVEC cells within 10 min (f and i; arrows) but not in SLURP1-treated cells, where it remained within the cytoplasm even after 30 min of treatment (o and r; arrowheads). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)