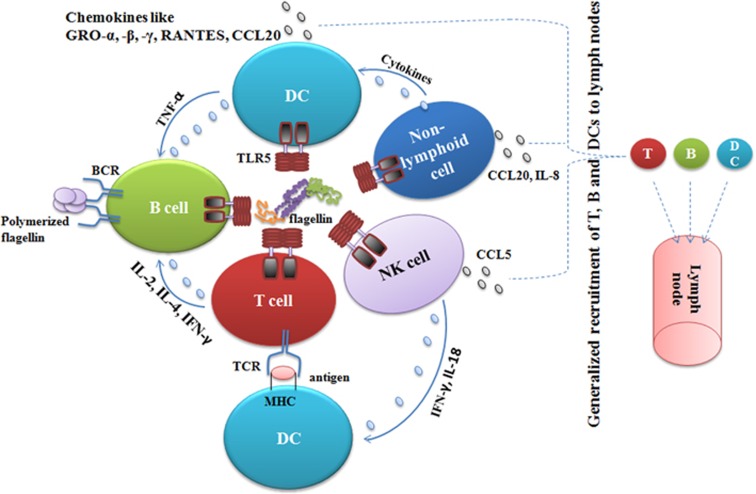
Figure 3.
Flagellin interactions with different kinds of immune and non-immune cells. Flagellin directly activates a number of immune and non-immune cells, including T, B, DCs, NK and non-lymphoid cells (macrophages, epithelial, fibroblasts, stromal cells and neutrophils), through TLR5. The cumulative effect of this activation is the augmentation of immune responses through the generation of more potent antibodies and a Th1 response. Moreover, the interaction of flagellin with TLR5 culminates in the production of chemokines from a number of lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells, which results in the generalized recruitment of T and B cells to LNs, which maximizes the chances of an encounter with their cognate antigen and subsequent elicitation of potent immune responses. Instead of TLR5, polymerized flagellin directly stimulates B cells by cross linking BCRs, which might generate antibody responses of the IgM type.