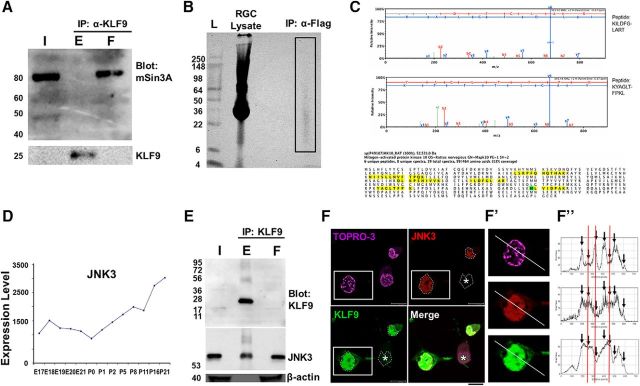
Figure 2.
KLF9 is bound by JNK3 in neurons. A, mSin3a is present in the retina but does not bind KLF9. Retina lysate from P10 rats was immunoprecipitated for KLF9 and Western blotted for mSin3a or KLF9. B, Purified P0 rat RGCs virally transduced with flag-tagged KLF9 were lysed and immunoprecipitated for flag. The IP lane (box) was sent for MS analysis. C, JNK3 is identified from KLF9 IP/MS. MAPK10/JNK3 was detected with six independent peptides (identified from eight unique and 19 total spectra with >95% confidence, yellow) and with 13% coverage (oxidized residue in green). D, JNK3 mRNA expression (arbitrary units) in developing RGCs from a previously described microarray dataset (Wang et al., 2007) shows robust upregulation during development. E, Endogenous KLF9 co-IPs with JNK3. Retinas from P10 rats were immunoprecipitated for KLF9 and Western blotting for anti-KLF9, anti-JNK3, and anti-β-actin antibodies, as marked. F, Confocal nanoscopy imaging of GFP-KLF9- and Flag-JNK3-electroporated RGCs demonstrated nuclear colocalization. Asterisk indicates that not all cells were successfully cotransfected. Fluorescence intensity of KLF9, JNK3, and TOPRO-3 were calculated separately and compared along the line in the cell cotransfected with both proteins (F′, arrows). Intensities showed higher similarity between KLF9 and JNK3 thanTOPRO-3 (red lines). F′′, High-magnification images of the boxed area in F. Scale bar, 10 μm. I, input; E, eluent; F, flow-through.