Figure 3.
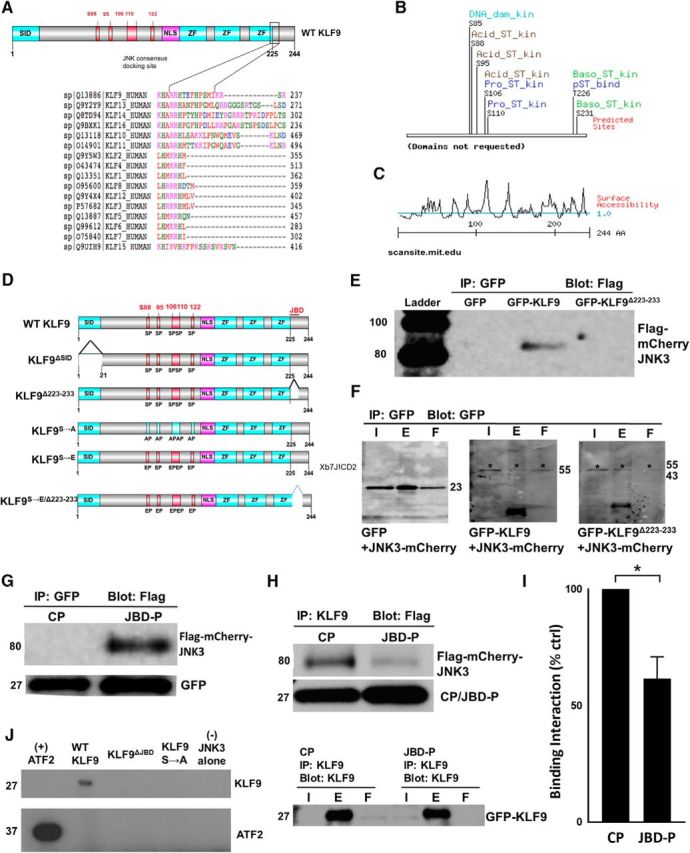
Identification of JNK3-binding domain and potential serine/threonine phosphorylation sites of KLF9. A, KLF9 structural analysis revealing potential JNK3-binding domains. ClustalW2 alignment shows region spanning R223 to I233 near C terminus of KLF9, as well as similar regions on subfamily relatives KLF13, KLF14, and KLF16, as well as KLF10 and KLF11, closely conforming to the known consensus JNK3 “DEJL” docking domain. B, MIT Scansite surface analysis of KLF9 full-length protein reveals potential phospho-acceptor sites at S88, S95, S106, and S110. C, MIT Scansite-predicted surface accessibility of KLF9 protein (>1 indicates exposed residues; <1 indicates buried or inaccessible residues). D, Schematic of a subset of mutant constructs for KLF9. ZF, Zinc finger domains. E, F, R223–I233 of KLF9 is necessary for KLF9–JNK3 interaction in neurons. E18 hippocampal neurons were cotransduced with Flag-mCherry-JNK3 and GFP, GFP-KLF9, or GFP-KLF9 R223-I233 deletion mutant (GFP-KLF9 Δ223–233) constructs using lentivirus. Cells were immunoprecipitated for GFP and Western blotted for flag (E) or GFP (F). G, H, JBD-P of KLF9 is sufficient for KLF9/JNK3 interaction in neurons. E18 hippocampal neurons were virally cotransduced with Flag-mCherry-JNK3 and either CP or JBD-P constructs (G), immunoprecipitated for GFP and Western blotted for flag. Flag-mCherry-JNK3 was only detected with the JBD-P construct (G). H, I, JBD-P reduces KLF9–JNK3 interaction. E18 hippocampal neurons were virally cotransduced with GFP-KLF9, Flag-mCherry-JNK3, and the CP or JBD-P, immunoprecipitated for KLF9, and Western blotted for flag or GFP (I). Densitometry quantification of blot bands showed an average of 38% decrease in the amount of flag-mCherry-JNK3 pulled down by the JBD-P coexpression group compared with the CP condition (I). J, KLF9 incorporation of radiolabeled [γ-32P] ATP depends on JNK-binding domain (JBD) and identified serine residues. E18 hippocampal neurons were transduced with flag-tagged wild-type KLF9, KLF9ΔJBD, or KLF9S85/88/95/106/110A mutants. Cells were immunoprecipitated for flag. Eluents were combined with recombinant JNK3 and radiolabeled [ϒ-32] ATP in a standard in vitro kinase assay. Incorporation of radioactivity was only observed in the eluents from wild-type KLF9 transduced neurons. *p < 0.05, 2-tailed Student's t test, n = 3. Error bars indicate SD. I, Input; E, eluent; F, flow-through.
