Fig. 1.
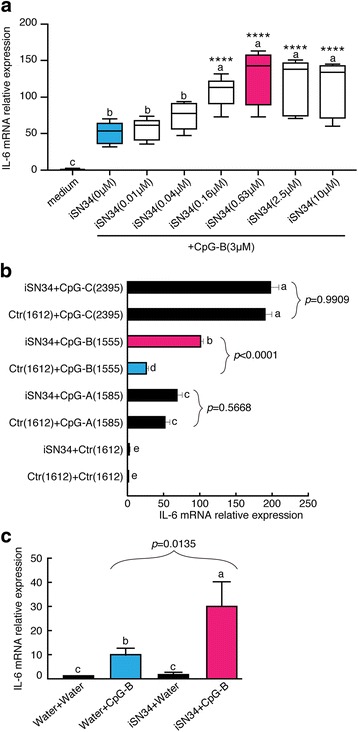
iSN34 was used to determine the optimal concentration of ODNs. a Mouse splenocytes were pre-incubated in medium for 3 h prior to exposure to iSN34 (at 0.01, 0.04, 0.16, 0.63, 2.5, or 10 μM) + CpG-B (ODN1555; at equimolar levels) or to ODN 1612 (control) for 6 h. Accumulation of IL-6 mRNA was determined by qPCR. Results are shown as the ratio of IL-6 mRNA levels for stimulated (iSN + CpG-B) versus ODN 1612-treated cells. b The synergistic effects of iSN34 (0.63 μM) were assessed in combination with CpG-A (ODN 1585), CpG-B (ODN 1555), CpG-C (ODN 2395), and Ctr 1612 (Control ODN). c Mouse splenocytes (1 × 107 cells/mL) were pre-incubated in medium for 3 h prior to exposure to 3 μM ODN 1612 or iSN34 for 24 h. Cells then were washed with medium (to remove the ODNs) and resuspended in medium with 3 μM CpG-B (ODN 1555) for 6 h. Results are shown as IL-6 mRNA expression (normalized to β-actin-encoding mRNA; see qPCR method) in stimulated cells in the wash-out assay. All assays were carried out at least three independent times in triplicate. Similar results were obtained from at least three different mice. Values are presented as mean + SD of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate (n = 9). Values with different letters (i.e., a, b, c, d, and e) were significantly different. ****p < 0.0001 vs. iSN34 (0 μM)
