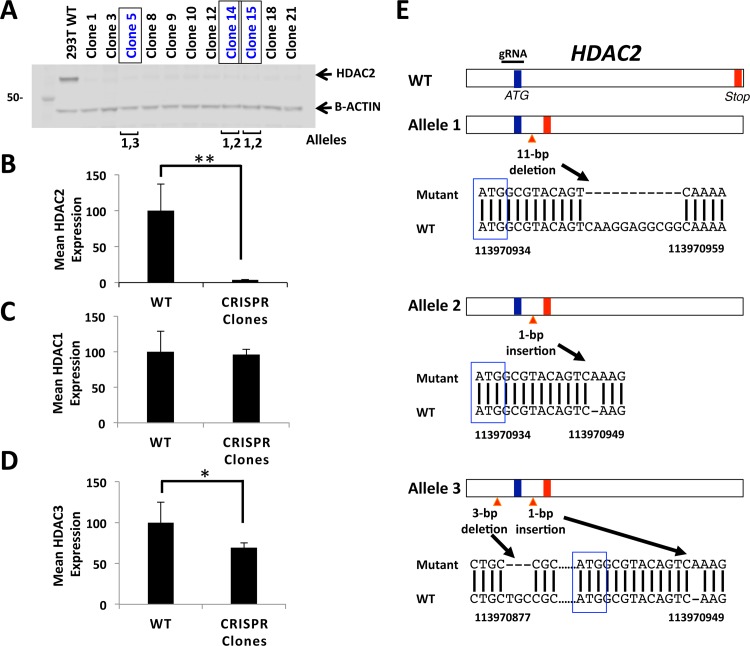
Fig 1. CRISPR-Cas9 disruption of HDAC2 in human cells.
(A) Nuclear lysates of a panel of HDAC2 targeted independent clonal lines generated through transfection of 293FT cells with CRISPR-Cas9 guide-RNA expressing plasmids targeting the first ‘ATG’ of HDAC2 were analyzed by Western blotting, demonstrating a complete or near complete loss of HDAC2 protein. (B) A larger panel of 21 HDAC2-targeted clonal lines demonstrated an overall mean 97% reduction in HDAC2 protein levels compared to WT HDAC2 protein (p<0.001). See S2A–S2C Fig for additional individual clone HDAC2 protein level data. (C) Mean HDAC1 protein levels in a panel of 13 HDAC2 null clonal lines demonstrated no significant change compared to HDAC1 protein levels in WT control. See also S2D and S2E Fig. (D) Mean HDAC3 protein levels for a panel of 13 HDAC2 null clonal lines demonstrated an overall mean 31% reduction of HDAC3 protein levels compared to WT cells (p<0.05). See also S2F and S2G Fig. All protein levels were normalized to B-actin. (E) Genomic DNA was isolated from three independent candidate gene edited clonal lines, PCR-amplified for HDAC2, and sequenced to detect and characterize any Indels present in each line. Three distinct alleles were identified. Allele 1 harbors a 11-bp deletion 3’ of the first ATG, Allele 2 has a 1-bp insertion 3’ of the first ATG, and Allele 3 has a 3-bp deletion 5’ of the first ATG and a 1-bp insertion 3’ of the first ATG. All three alleles result in a premature stop codon (both WT and Indel-induced stop codons are indicated as red vertical lines, while start codons are indicated by blue vertical lines). The three clonal lines of focus for this study overall are indicated by brackets in panel (A): clone 5 has alleles 1 and 3, while clonal lines 14 and 15 have alleles 2 and 3.