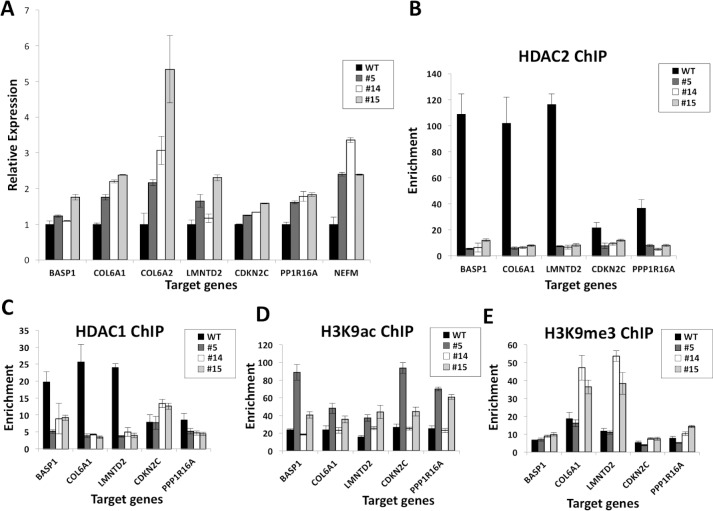
Fig 4. HDAC2 is required for HDAC1 recruitment to validated HDAC2-repressed target genes and in HDAC2 nulls these targets display altered histone H3K9 modifications.
(A) qPCR validation of candidate targets of HDAC2 repression as determined by RNA-seq. Gene expression of WT or the three clonal null lines (#5, #14 and #15) was internally normalized to GAPDH and fold enrichment represented relative to WT. All three null lines exhibited significantly elevated target gene expression for COL6A2, LMNTD2, NEFM, and PPP1R16A (p<0.05 in each case), and for CDKN2Cand COL6A1 (p<0.001 for both), but BASP1 expression was significantly changed (p<0.05) only in clone #15. Error bars are S.E.M. (B-F) ChIP-qPCR was conducted on crosslinked chromatin of WT and clones #5, #14, and #15 with antibodies to HDAC2 (B), HDAC1 (C), H3K9ac (D), H3K9me3 (E) or IgG control and qPCR analysis was conducted to evaluate the binding of HDAC2 or HDAC1 or enrichment of the specified histone marks at the promoter regions of the genes indicated. Enrichment was calculated by normalization to input and IgG control samples and plotted as mean of n = 3 with error bars representative of S.E.M.