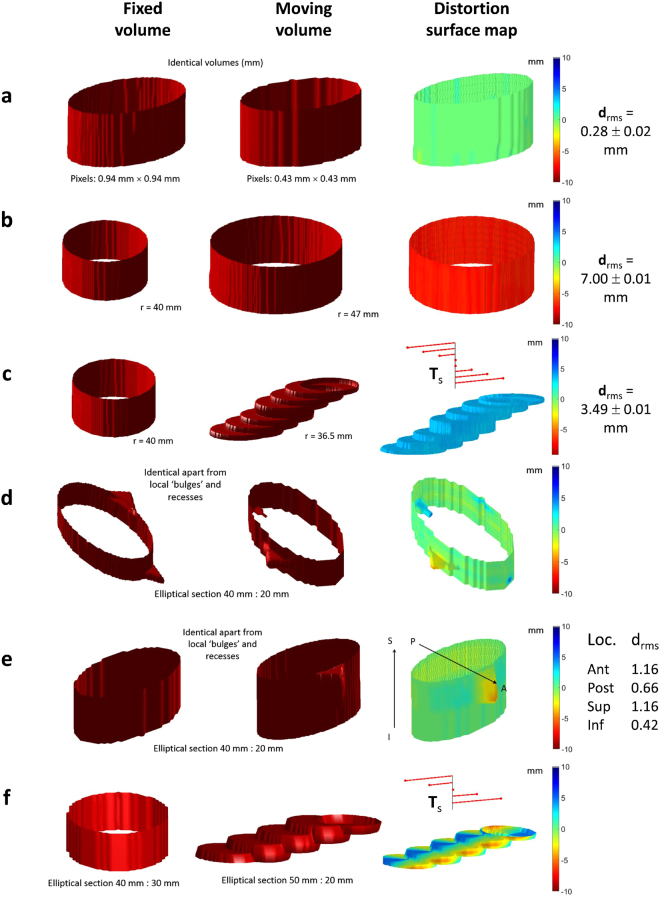
Figure 3.
Examples of virtual phantoms used to validate the algorithm quantifying distortion. (a) identical volumes (as measured in mm) in dissimilar spaces; (b) volumes constructed from circular outlines of differing radii: d rms reflects the difference in radii and the surface distortion map is coloured red indicating that the moving volume surface bulges from the fixed volume surface uniformly; (c) step-wise local translation of centroids is reflected in T s tree while local distortion reflects the uniform recess due to circular sections in moving volume being smaller than those in fixed volume; (d) local bulges in otherwise identical volumes are reflected in colour of distortion surface map; (e) similar to (d) but showing an anterior and superior bias in distortion; (f) local translation and slice section difference in shape reflected in distortion surface map and T s tree respectively.