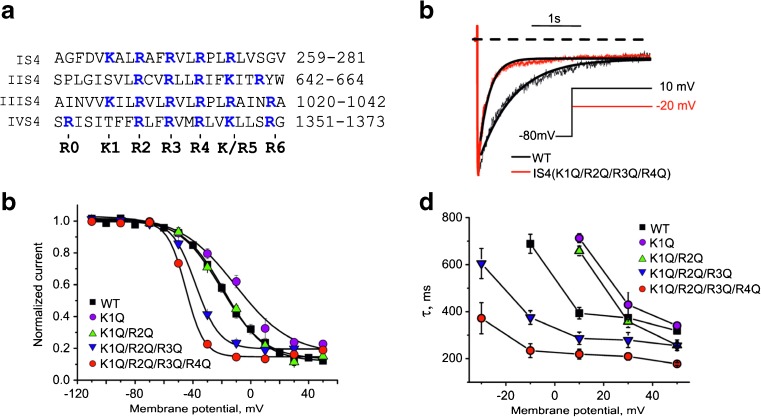
Fig. 1.
Neutralization of segment IS4 modulates Cav1.2 inactivation. a Alignment of Cav1.2 segments IS4-IVS4. Charged residues are highlighted in blue. b Superimposed typical normalized IBa through WT and mutant IS4(K1Q/R2Q/R3Q/R4Q). IBa through WT and quadruple mutant IS4(K1Q/R2Q/R3Q/R4Q) during 3 s depolarizations from −80 mV to the voltages of the maximum of the current-voltage relationship (WT: 10 mV; IS4(K1Q/R2Q/R3Q/R4Q): −20 mV). Note the faster development of inactivation in IS4(K1Q/R2Q/R3Q/R4Q). Current decay was fitted to a monoexponential function yielding time constants of τ inact(WT) = 393 ± 24 ms and τinact(IS4(K1Q/R2Q/R3Q/R4Q)) = 235 ± 29 ms, respectively (see “Methods”). Solid lines represent the fitted function. c Steady-state inactivation curves of WT and the indicated IS4 mutants. Voltages of half-maximal inactivation (V 0.5,inact) where −18.3 ± 1.1 mV (WT), −13.2 ± 3.5 mV (IS4(K1Q)), −20.3 ± 1.2 mV (IS4(K1Q/R2Q)), −38.1 ± 0.8 mV ((IS4(K1Q/R2Q/R3Q)), and −45.0 ± 0.7 mV ((IS4(K1Q/R2Q/R3Q/R4Q)). d Inactivation time constants (τ inact) at different voltages were obtained by fitting the IBa decay over an interval of 3000 ms by a mono-exponential function. Time constants for WT and the indicated IS4 mutants are plotted as function of the membrane potential