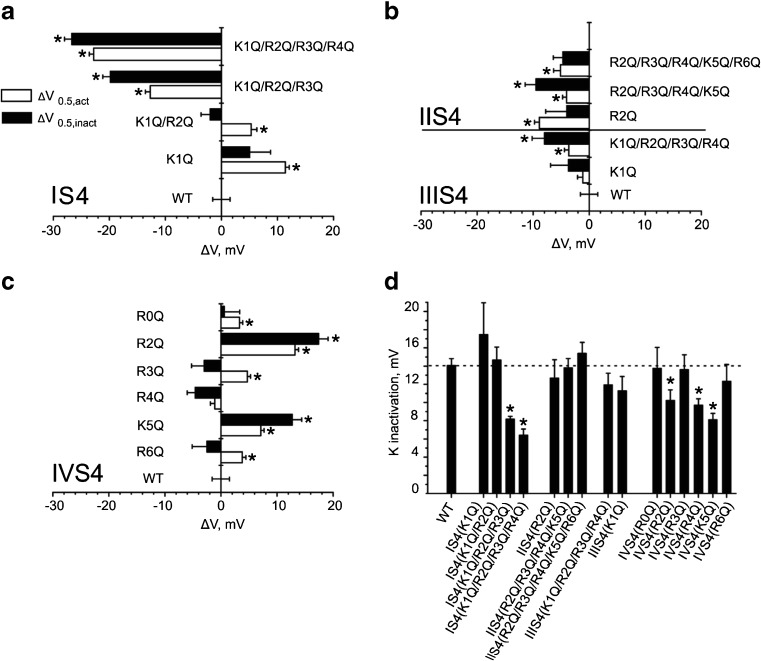
Fig. 4.
Charge neutralizations in Cav1.2 segments IS4–IVS4 differently affect the position and slope of the inactivation curve. a–c Shifts of the midpoint voltages (V 0.5,inact closed bars,V 0.5,act open bars) of a IS4 , b IIS4 and IIIS4, and c IVS4-mutants compared to WT. d Slope factors of inactivation curves were significantly (*p < 0.05) decreased by charge neutralization in IS4 and IVS4. Strongest changes were observed for mutants IS4((K0Q/R1Q/R2Q) with k inact. = 8.2 ± 0.6 mV; IS4(K1Q/R2Q/R3Q/R4Q) with k inact. = 6.2 ± 0.7 mV; IVS4(R2Q) with k inact. = 10.2 ± 1.2 mV; IVS4(R4Q) with k inact. = 9.7 ± 0.7 mV and IVS4(K5Q) with k inact. = 8.1 ± 0.7 mV. Neutralization of either single or combined charge neutralizations in IIS4 and IIIS4 had no significant effect on the slope factors of steady-state inactivation curves (Table 1)