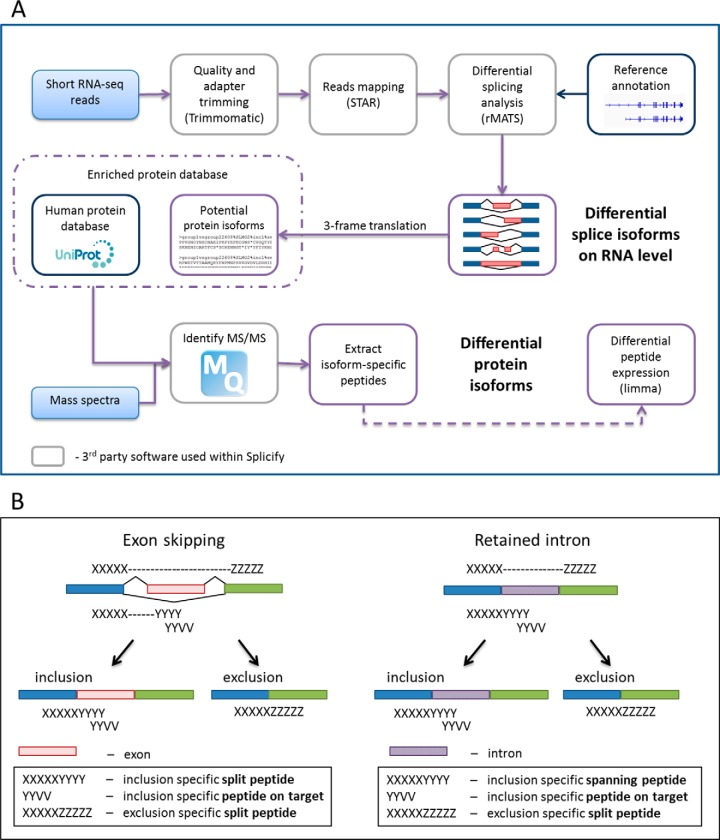
Fig. 1.
Splicify, the proteogenomic pipeline for identification of differential splice variants. A, The schematic overview of the Splicify data analysis. Within Splicify RNA-seq data analysis is performed by combining exemplar open-source RNA-seq analysis software, including quality and adapter trimming with Trimmomatic (36), reads mapping with STAR (38), differential splicing analysis with rMATS (37), where differential splice variants on RNA level are identified. These splice variants undergo 3-frame translation into potential protein isoform sequence database (FASTA). This database together with the human protein database from Uniprot (39) can be further used with MaxQuant (40), a search engine to identify MS/MS spectra originating from the same samples as RNA-seq reads. Downstream analysis of MaxQuant output is performed with the use of the results from RNA-seq analysis. Isoform-specific peptides are extracted and quantified and based on these peptides differential protein isoforms are identified. Splicify produces a final table with both RNA and protein isoform information. B, Example of peptides supporting translation of splicing events for skipped exon and retained intron. Split peptides map to both sides of an exon-exon junction, spanning peptides span exon-intron junctions (specific for inclusion variants for retained intron, alternative 3′ and 5′ splice sites) and peptides on target map to a spliced fragment.