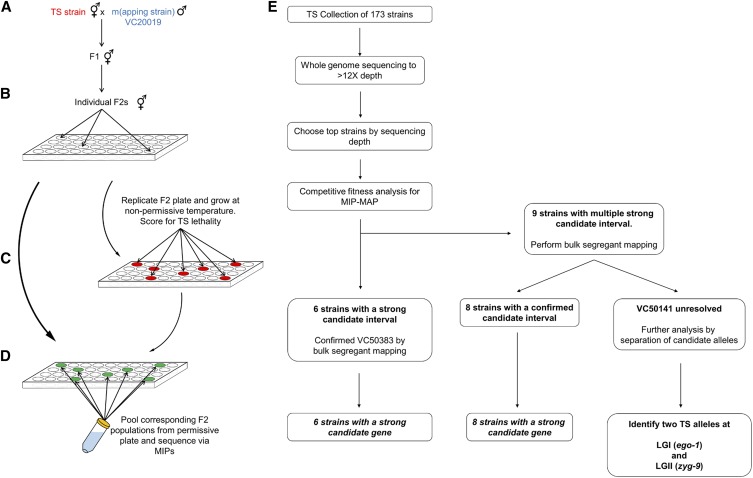
Figure 3.
Workflows for liquid bulk segregant mapping and TS mutant analysis. (A) VC20019 males were mated to a TS mutant strain with cross-progeny F1 animals used to generate F2 recombinants. Single F2s were used to seed wells (B), growing these populations at permissive temperatures before replicating them to grow in nonpermissive conditions (C) and identifying populations that failed to thrive. Dead populations (red) were then chosen from the original wells (green) and pooled together (D) to prepare a single genomic sample for MIP-MAP sequencing. Samples from multiple plates were combined in the mapping of a single mutant depending on allele penetrance or the number of positive F2 wells identified. The workflow (E) of mapping TS mutants shows six strains could be mapped by competitive fitness MIP-MAP alone, eight strains benefitted from additional mapping via the liquid bulk segregant protocol, and one strain (VC50141) required additional analyses. MIP-MAP, molecular inversion probe mapping; TS temperature-sensitive.