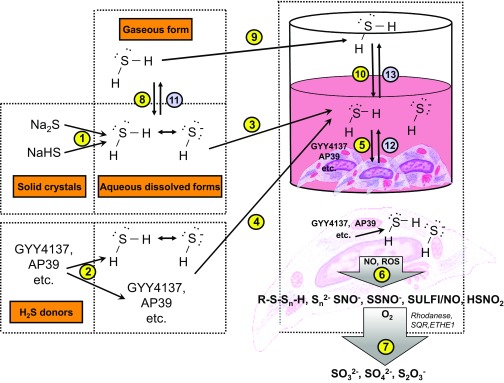
Fig. 2.
H2S delivery to cell in culture. H2S and HS− are immediately generated when rapid-release H2S donors (i.e., sulfide salts) are dissolved in aqueous stock solutions (1). Likewise, when H2S donors (e.g., GYY4137, AP39 etc.) are dissolved in solution, some H2S and HS− can already begin to form (the extent of which depends on the chemical properties of the donor) (2). When stock solutions are added to the cell culture medium, these species (H2S-donor molecules, H2S and HS−) are delivered, first into the medium (3,4) and from there into the cultured cells (5). Some donors themselves are hydrophilic and may not have high cell permeability; these donors are likely to remain extracellular, and the H2S produced from them will enter the cells. Other H2S donors may enter the cells more readily (some of them may be cell-compartment-specific, e.g., AP39 sequesters into the mitochondria and delivers H2S preferentially to the mitochondrial component). Intracellularly, production is via glutathione-dependent conversion mechanisms. Intracellularly, H2S will react with various molecules (proteins, thiols, nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species) to create a mixture of biologically active species (polysulfides, persulfides, hybrid S/N compounds). Some of these reactions, e.g., with proteins and thiols, will already occur extracellularly in the cell culture medium (not shown) (6). Thus the cellular effects of H2S donors are produced by a complex array of interactions and biological actions induced by multiple species. H2S decomposition products (sulfite, sulfate, thiosulfate) are also produced via enzymatic and nonenzymatic processes (7). Another way to deliver H2S is by bubbling H2S into aqueous solutions (for instance, the method was used to produce IK-1001) (8). This solution, then, can be added to cells the same way as the other H2S delivery approaches (3). One can also supply H2S gas into the cell culture headspace, which, in turn, dissolves in the culture medium (9, 10) and delivers H2S and HS− to the cells. As soon as the H2S donors are dissolved in the stock solution, H2S starts to escape through diffusion into the air (11). Loss of H2S will also occur through diffusion of H2S from the cells into the culture medium (12) and then into the headspace (13).